B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 3: DPP
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 3: DPP
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 1: Ray Optics, Exercise 3: DPP with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Optics and Modern Physics JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 3: DPP with Hints & Solutions
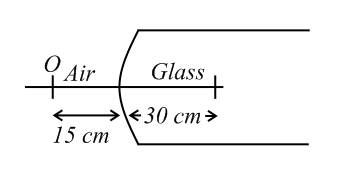
A point object is placed in front of a glass rod having spherical end of radius of curvature The image would be formed at
A glass hemisphere of radius made up of material with a refractive index is placed centrally over a cross mark on a paper
(i) with the flat face
(ii) with the curved face in contact with the paper.
In each case, the cross mark is viewed directly from above. The position of the images will be
An air bubble in sphere having a diameter appears to be at from surface nearest to eye when looked along diameter. If , the distance of bubble from refracting surface is
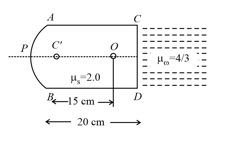
The slab of a material of refractive index , as shown in the figure, has curved surface of radius of curvature and a plane surface . On the left of is air and on the right of is water with refractive indices as given in the figure. An object is placed at a distance of from pole as shown. The distance of the final image of from as viewed from the left is
A parallel beam of light emerges from the opposite surface of the sphere when a point source of light lies at the surface of the sphere. The refractive index of the sphere is
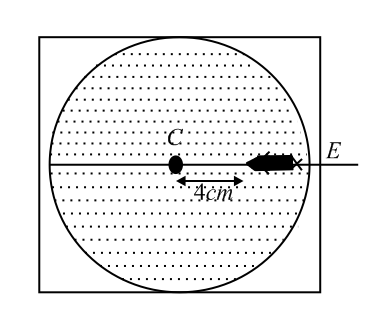
In a thin spherical fish bowl of radius filled with water of refractive index , there is a small fish at a distance of from the centre as shown in the figure. Where will the image of fish appear, if seen from ?
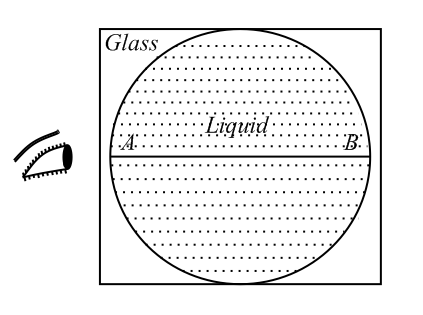
The observer sees the distance as infinitely large. If the refractive index of the liquid is and that of glass is then is
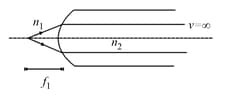
The first focal length for refraction at a spherical surface is defined as the value of corresponding to (as shown) with refractive indices of two mediums as and . The second focal length is defined as value of for (where is the radius of the curved surface). Choose the correct option(s).