B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 7: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS FOR JOINT ENTRANCE EXAMINATION WAVES AND THERMODYNAMICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with Hints & Solutions
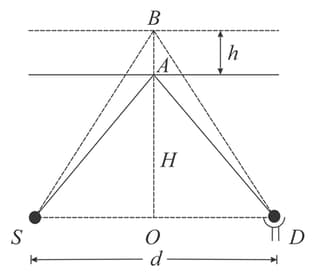
A source and a detector of high frequency waves are a distance apart on the ground. Maximum signal is received at when the reflecting layer is at a height When the layer rises a distance no signal is detected at Neglecting absorption in the atmosphere, find the relation between and the wavelength of the waves.
Two waves have the same frequency. The first has intensity The second has intensity and lags behind the first in phase by When they meet, find the resultant intensity, and the phase relationship of the resultant wave with the first wave.
A travelling wave has speeds and in two different media and Such a wave travelling through gets incident normally on a plane boundary, separating and Find the ratio of amplitudes of the reflected and transmitted waves.
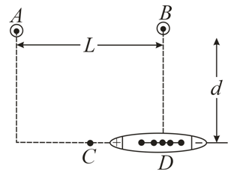
The ship in figure travels along a straight line parallel to the shore and a distance from it. The ship's radio receives simultaneous signals of the same frequency from antennas and separated by a distance The signals interfere constructively at point which is equidistant from and The signal goes through the first minimum at point which is directly outward from the shore from point Determine the wavelength of the radio waves.
Two wires of different linear mass densities are soldered together end to end and then stretched under a tension The wave speed in the first wire is thrice than in the second. If a harmonic wave travelling in the first wire is incident on the junction of the wires and if the amplitude of the incident wave is, find the amplitude of reflected wave.
The pulse shown in figure has a speed of If the linear mass density of the right string is that of the left string, find the ratio of the height of the transmitted pulse to that of the incident pulse.
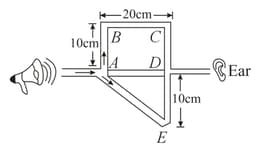
The figure shows a tube structure in which a signal is sent from one end and is received at the other end. The frequency of the sound source can be varied electronically between, and Find the frequencies at which maxima of intensity are detected. The speed of sound in air,
In Quinck's acoustic interferometer, it is found that the sound intensity has a minimum value of, units at one position of the sliding tube, and continuously climbs to a maximum of , units at a second position, from the first. Find
The frequency of the sound emitted by the source and,
The relative amplitudes of the two waves arriving at the detector. The velocity of sound in air
