B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 45: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 9.3
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 45: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 9.3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Circular Motion, Exercise 45: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 9.3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced) Mechanics I solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 45: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 9.3 with Hints & Solutions
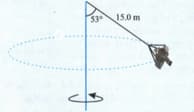
A large mass and a small mass hang at the two ends of a string that passes over a smooth tube. The mass m moves around a circular path which lies in a horizontal plane. The length of the string from the mass to the top of the tube is and is the angle the length makes with the vertical. What should be the frequency of rotation of the mass so that the mass remains stationary?
An race car can drive around an unbanked turn at a maximum speed of without slipping. The turn has a radius of curvature of . Air flowing over the car exerts a downward-pointing force (called the downforce) of on the car.
(a) What is the coefficient of static friction between the track and the car’s tires?
(b) What would be the maximum speed if no downforce acted on the car?
A swing ride at a carnival consists of chairs that are swung in a circle by cables attached to a vertical rotating pole as the drawing shows. Suppose the total mass of a chair and its occupant is .
(a) Determine the tension in the cable attached to the chair.
(b) Find the speed of the chair.
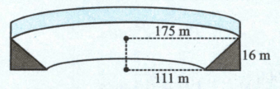
On a banked race track, while the largest path has a radius of , the smallest circular path on which cars can move has a radius of as the drawing illustrates. The height of the outer wall is .
(a) the smallest and
(b) the largest speed at which cars can move on this track without relying on friction.
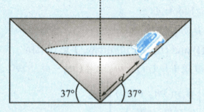
A racetrack has the shape of an inverted cone as the drawing shows. On this surface, the cars race in circles that are parallel to the ground. For a speed of , at what value of the distance should a driver locate his car if he wishes to stay on a circular path without depending on friction?
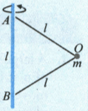
A particle of mass is connected with two inextensible strings and of equal a lengths . These two strings are finally attached to a vertical rod at points and as shown in figure. Distance between and is also . The setup is rotated with constant angular speed with rod as the axis.
(a) Find the values of for which the particle remains at point .
(b) Find the range of values of for which tension in the string is greater than but the other string remains slack.
(C) Find the value of for which tension in string is twice the tension in the string .
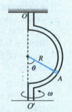
A sleeve can slide freely along a smooth rod bent in the shape of a half circle of radius . The system is set in rotation with a constant angular velocity about a vertical axis . Find the angle corresponding to the steady position of the sleeve.
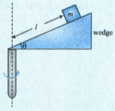
A small wedge whose base is horizontal is fixed to a vertical rod as shown in the figure. The sloping side of the wedge is frictionless and the wedge is spun with a constant angular speed about vertical axis as shown in the figure. Find
(a) the value of angular speed for which the block of mass just does not slide down the wedge,
(b) the normal reaction on the block by wedge when block does not slip relative to wedge.