B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: Concept application Excercise
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: Concept application Excercise
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: Concept application Excercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS for Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced) Electrostatics and Current Electricity solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electrical Measuring Instruments, Exercise 1: Concept application Excercise with Hints & Solutions
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance gives a full-scale deflection when a current of is passed through it. It is to be converted into an ammeter reading on a full scale. But the shunt of , only is available. What resistance should be connected in series with the galvanometer coil?
In the circuit in figure ammeter and voltmeter are ideal If and , find the readings of ammeter and voltmeter.
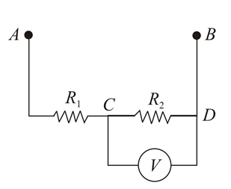
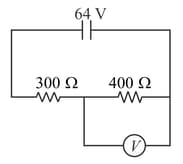
Resistances and each are connected in series. The potential difference between points and is . Find the reading of the voltmeter connected between points and if its resistance .
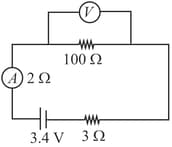
A cell of emf and internal resistance is connected to an ammeter having resistance and to an external resistance of . When a voltmeter is connected across the resistance, the ammeter reading is . Find the voltage reading by the voltmeter and its resistance. Had the voltmeter been an ideal one what would have been its reading?
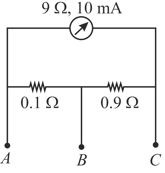
A milliammeter of range and resistance is joined in a circuit as shown. The meter gives full-scale deflection for current when and are used as its terminals, i.e., current enters at and leaves at ( is left isolated). Find the value of .
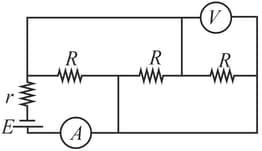
In the circuit, a voltmeter reads , when it is connected across resistance. Calculate what the same voltmeter will read when it is connected across the resistance?
A galvanometer (coil resistance ) is converted into an ammeter using a shunt of and connected as shown in the figure . The ammeter reads . The same galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter by connecting a resistance of in series. This voltmeter is connected as shown in the figure . Its reading is found to be of the full-scale reading. Find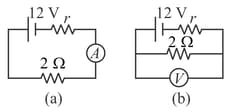
The internal resistance of the cell.
Range of the ammeter and voltmeter.
Full-scale deflection current of the galvanometer.
A battery of emf and internal resistance is connected to a resistor of resistance through an ammeter. The resistance of the ammeter is . A voltmeter has also been connected to find the potential difference across the resistor.
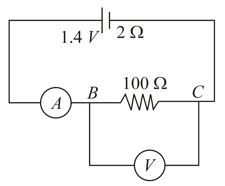
The ammeter reads . What is the resistance of the voltmeter?
