B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 3: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 3: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 3: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced): Mechanics II solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 3: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with Hints & Solutions
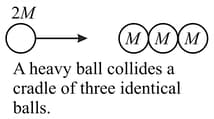
A heavy ball of mass moving with a velocity collides elastically head-on with a cradle of three identical balls each of mass as shown in figure. Determine the velocity of each ball after collision.
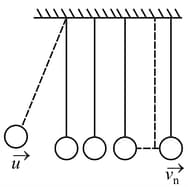
In figure, there are identical spheres of mass suspended with wires of equal length. The spheres are almost in contact with each other. Sphere is pulled aside and released. If sphere strikes sphere with velocity find an expression for velocity of the sphere immediately after being struck by the one adjacent to it. The coefficient of restitution for all the impacts is
A mass moves with a great velocity. It strikes another mass at rest in head-on collision. It comes back along its path with low speed after collision. Then find out whether or
A ball of mass moving with a velocity of impinges directly on another ball of mass moving with velocity of in the same direction. Find their velocities after impact and calculate the loss of due to impact if
Three balls of masses and are lying in a straight line. The first ball is moved with a certain velocity so that it strikes the second ball directly and itself comes to rest. The second ball collides with the third and is itself reduced to rest. If is the coefficient of restitution for each ball, write down the relation of in terms of and
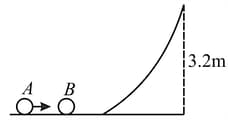
Two identical balls and lie on a smooth horizontal surface, which gradually merges into a curve to a height Ball is given a velocity of to collide head-on with ball which then takes up the curved path. What is the minimum coefficient of restitution, for the collision between and in order that ball reaches the highest point of the curve.
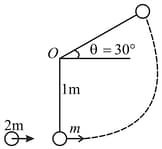
A smooth ball of mass is suspended from a light string of length Another ball of mass strikes the ball of mass horizontally with a speed of . The coefficient of restitution for the collision is The string becomes loose, when it makes an angle of with the horizontal; find the value of Use .
Two balls of masses and and momenta and collides as shown in figure. During collision, the value of linear impulse between them is In terms of and find coefficient of restitution ' '. Under what condition collision is elastic. Also find the condition of perfectly inelastic collision.

