B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 6: Exercises
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 6: Exercises
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 6: Exercises with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced): Mechanics II solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Impulse and Collision, Exercise 6: Exercises with Hints & Solutions
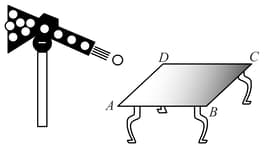
A gun which fires small ball of mass is firing balls per second on the smooth horizontal table surface . If the collision is perfectly elastic and balls are striking at the centre of table with a speed at an angle of with the vertical just before collision, then force exerted by one of the leg on ground is (assume total weight of the table is and ):-
A ball strikes a smooth horizontal floor obliquely and rebounds inelastically.
A particle suffers an oblique elastic collision with a particle that is at rest initially. If their masses are the same, then after the collision
A ball strikes a wall with a velocity at an angle with the normal to the wall surface and rebounds from it at an angle with the surface. Then
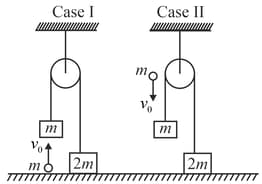
Two masses, and are connected by an inextensible light string. The string is passing over a light frictionless pulley. The mass is resting on a surface and mass is hanging in the air as shown in the figure. A particle of mass, strikes the mass, from below in case with a velocity and in case strikes mass with a velocity from top and sticks to it.
A body of mass moving with a velocity collides with a body of mass moving with a velocity of in opposite direction. If the collision is head on and completely inelastic, then
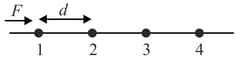
The diagram shows a string of equally placed beads of mass , separated by distance . The beads are free to slide without friction on a thin wire. A constant force acts on the first bead initially at rest till it makes collision with the second bead. The second bead then collides with the third and so on. Suppose that all collisions are elastic.
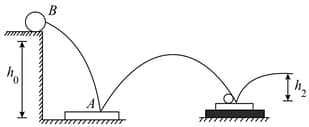
A ball dropped from a height reaches a height after bouncing twice from identical plates. Plate A rests directly on hard ground, while plate rests on a foam -rubber mat. Determine.
(ii) the height of the ball's first bounce.