B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Surface Tension and Viscosity, Exercise 6: Exercises
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Surface Tension and Viscosity, Exercise 6: Exercises
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Surface Tension and Viscosity, Exercise 6: Exercises with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced): Mechanics II solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Surface Tension and Viscosity, Exercise 6: Exercises with Hints & Solutions
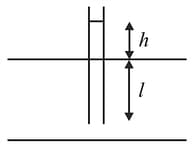
When a capillary tube is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises to a height in the tube. The free liquid surface inside the tube is hemispherical in shape. The tube is now pushed down so that the height of the tube outside the liquid is less than
Two separate bubbles (radii and ) formed of the same soap solution (surface tension ) comes together to form a double bubble. The internal film common to both the bubbles has radius . Then,
The velocity of liquid $(v)$ in steady flow at a location through cylindrical pipe is given by $v=v_{0}\left(1-\frac{r^{2}}{R^{2}}\right)$, where $r$ is the radial distance of that location from the axis of the pipe and $R$ is the inner radius of pipe, if $R=10 \mathrm{~cm}$, volume rate of flow through the pipe is $\pi / 2 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~m}^{3} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$ and the coefficient of viscosity of the liquid is $0.75 \mathrm{~N} \mathrm{~s} \mathrm{~m}^{-2}$
A water drop and a mercury drop is taken inside identical horizontal conical glass pipes. Then
A long thin walled capillary tube of mass and radius is partially immersed in a liquid of surface tension . The angle of contact for the liquid and the tube wall is . How much force(in ) is needed to hold the tube vertically? Neglect buoyancy force on the tube.
(Take , )
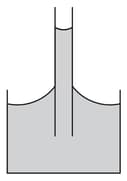
A tapering glass capillary tube of length has diameters and at the ends. When it is just immersed in a liquid at with larger radius in contact with liquid surface, the liquid rises in the tube. In another experiment, in a cylindrical glass capillary tube , when immersed in the same liquid at , the liquid rises to height. The rise of liquid in tube is only when the liquid is at . Find the rate at which the surface tension changes (in ) with temperature considering the change to be linear. The density of liquid is and the angle of contact is zero. Effect of temperature on the density of liquid and glass is negligible.
There is an air bubble of radius in a liquid of surface tension and density . The bubble is at a depth of below the free surface. By what amount is the pressure (in Pa) inside the bubble greater than the atmospheric pressure? (Take )
The capillary tube is dipped in water vertically. It is sufficiently long so that water rises to maximum height in the tube. The length of the portion immersed in water is . The lower end of the tube is closed, the tube is taken out and opened again. Then, find the length of the water column (in ) remaining in the tube.