Internal Energy and Work Done in Thermodynamics
Important Questions on Internal Energy and Work Done in Thermodynamics
A non-conducting cylindrical vessel of length, is placed horizontally & is divided into three parts by two easily moving pistons having low thermal conductivity as shown in the figure. These parts contains and gad at initial temp. , and respectively. If the initial length and pressure of each part are and respectively, calculate the final pressure and length of each part. Use: .
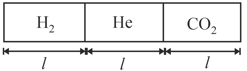
The pressure in monoatomic gas increases linearly from to when its volume increases from to .
(i) If work done by the gas is then find the value of .
(ii) If increase in internal energy is then find the value of .
(iii) If amount of heat supplied is then find the value of .
(iv) If molar specific heat of the gas is then find the value of .
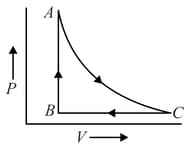
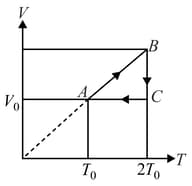
One mole of monoatomic ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process as shown in figure. Process is adiabatic. The temperatures at and are and respectively:-
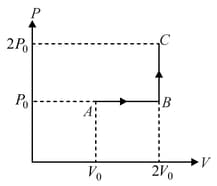
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is taken from to along the path The temperature of the gas at is For the process
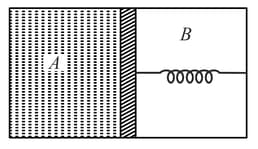
A thermally insulated chamber of volume is divided by a frictionless piston of area into two equal parts and . Part has an ideal gas at pressure and temperature and in part is vacuum. A massless spring of force constant is connected with piston and the wall of the container as shown. Initially spring is unstarched. Gas in chamber is allowed to expand. Let in equilibrium spring is compressed by . Then
An ideal monatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process as shown in the figure. The ratio of heat absorbed during to the work done on the gas during is:
An ideal gas is heated from temperature to under various conditions. The correct statement(s) is/are:-

