Photoelectric Effect
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect
When a metallic surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential is . If the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential is . The threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is:
When photon of wavelength is incident on a metal surface then speed of ejected fastest electron is . If photon of wavelength incident on the same metal then speed of ejected fastest electron is . Value of will be:-
The threshold frequency for a photo-sensitive metal is . If light of frequency is incident on this metal, the cut-off voltage for the photo-electric emission is nearly
In photoelectric emission process from a metal of work function the kinetic energy of most energetic electrons is . The corresponding stopping potential is
The frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive metal plate is doubled, the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is
A photocell employs photoelectric effect to convert
A photosensitive metallic surface has work function . If photons of energy falls on this surface, the electron come out with a maximum velocity of .When the photon energy is increased to , then maximum velocity of photoelectrons will be:
The work function of a surface of a photosensitive material is . The wavelength of the incident radiation, for which the stopping potential is , lies in the
A photoelectric surface is illuminated successively by monochromatic light of wavelength and If the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons in the second case is times that in the first case, the work function of the surface of the material is:
Radiation of wavelength , is incident on a photocell. The fastest emitted electron has speed . If the wavelength is changed to , the speed of the fastest emitted electron will be
When photons of energy- fall on an aluminium plate (of work function is ), photoelectrons of maximum kinetic energy are ejected. If the frequency of the radiation is doubled, the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons will be
In photoelectric effect, the electrons are ejected from metals if the incident light has a certain minimum
The total energy of an electron is 3.555 MeV, then its Kinetic energy is :-
An electron with (rest mass ) moves with a speed of . Its mass when it moves with this speed is
The velocity at which the mass of a particle becomes twice of its rest mass, will be -
Work function of potassium metal is . When the light of frequency is incident on the metal surface, photoemission of electrons occurs. The stopping potential of the electrons will be equal to
In a photoelectric experiment the graph of frequency of incident light (in ) and stopping potential (in volts) is shown below. From the figure the value of the Planck's constant is ( is the elementary charge)
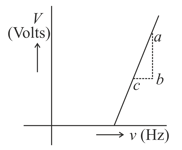
The work functions for metals A, B and C are respectively 1.92 eV, 2.0 eV and 5eV. According to Einstein’s equation, the metals which will emit photo electrons for a radiation ot wavelength 4100 is/are :-
The kinetic energy of most energetic electrons emitted from a metallic surface is doubled when the wavelength of the incident radiation is changed from 400 nm to 310 nm the work-function of the metal is :
The threshold wavelength of tungsten is . If ultraviolet light of wavelength is incident on it, then the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons would be-

