Genetic Modification
Important Questions on Genetic Modification
Many people in the world do not have enough vitamin A in their diet. We can make vitamin A in the body from carotene, which is found naturally in many plants. Rice has all the genes for making carotene, but some of these genes are turned off in the rice grains.
Researchers have added two genes to rice plants, which code for the production of two enzymes that enable the production of carotene in rice grains. Figure 20.1 shows how one of the genes, from a bacterium, was added.
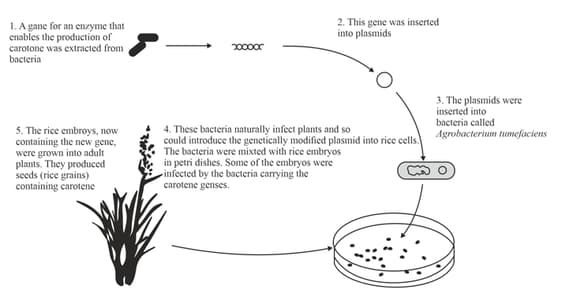
On figure 20.1, write the letter R at one step at which restriction enzymes would be used.
Many people in the world do not have enough vitamin A in their diet. We can make vitamin A in the body from carotene, which is found naturally in many plants. Rice has all the genes for making carotene, but some of these genes are turned off in the rice grains.
Researchers have added two genes to rice plants, which code for the production of two enzymes that enable the production of carotene in rice grains. Figure 20.1 shows how one of the genes, from a bacterium, was added.
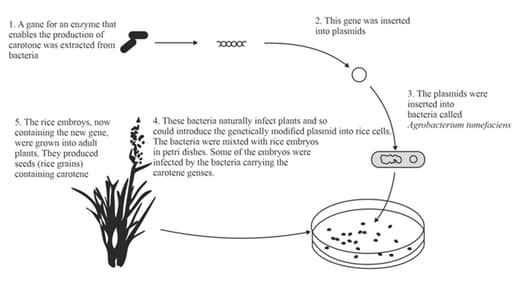
In figure 20.1, write the letter L to indicate one step at which DNA ligase would be used.
Explain the role of plasmids in the process of producing genetically modified rice.
Explain why it is useful to cut the DNA so that there are sticky ends.
Explain what is sticky ends are.
Use the information in the given figure 20.1, and your knowledge, to explain why Agrobacterium tumefaciens was used in this process.
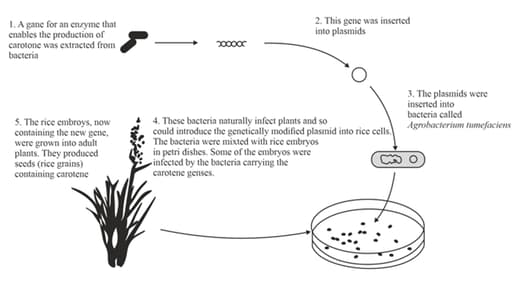
Figure. 20.1: Diagram showing how a gene was added to a rice plant.
Suggest why the researchers decided to produce this new form of rice by genetic modification, rather than selective breeding.
List three conditions that are controlled in the fermenter while Penicillium viridicatum is growing in it. For each condition, explain why and how it is controlled.
List three ways in which crop plants have been genetically modified.
Explain what is meant by the term genetic modification.

