Mary Jones, Richard Fosbery, Dennis Taylor and, Jennifer Gregory Solutions for Chapter: Control and Coordination, Exercise 5: Question
Mary Jones Biology Solutions for Exercise - Mary Jones, Richard Fosbery, Dennis Taylor and, Jennifer Gregory Solutions for Chapter: Control and Coordination, Exercise 5: Question
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 15: Control and Coordination, Exercise 5: Question with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Biology for Cambridge International AS & A Level coursebook 2nd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Mary Jones, Richard Fosbery, Dennis Taylor and, Jennifer Gregory Solutions for Chapter: Control and Coordination, Exercise 5: Question with Hints & Solutions
Describe how a neurone maintains resting potential.
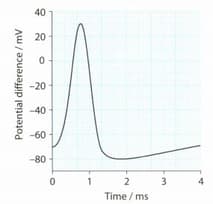
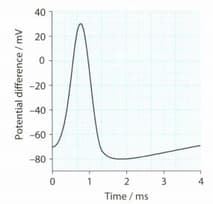
As an action potential begins, the potential difference changes from — 70 mV to +30 mV inside. Why is this called depolarisation?
As an action potential begins, the potential difference changes from — 70 mV to + 30m V inside. Annotate a graph to describe what is happening in the axon membrane to cause this depolarisation.
Annotate the given graph to describe what is happening between 1 ms and 2 ms.
If the action potential starts at time 0, how long does it take for the resting potential to be restored?
Indicate the refractory period on the given graph.
What is the role of the refractory period?
Ouabain is a poison that stops the activity of sodium- potassium pumps. If ouabain is added to part of an axon at a specific place along an axon, action potentials can continue to pass that region for about 1000 impulses. Suggest why they do not stop immediately.