M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Heron's Formula, Exercise 1: Exercise 12.1
M L Aggarwal Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Heron's Formula, Exercise 1: Exercise 12.1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 12: Heron's Formula, Exercise 1: Exercise 12.1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CBSE Syllabus Standard Mathematics for Class IX solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Heron's Formula, Exercise 1: Exercise 12.1 with Hints & Solutions
Write whether the following statement is true or false. Justify your answer.
If the base and the corresponding altitude of a parallelogram are and respectively, then the area of the parallelogram is .
Write whether the following statement is true or false. Justify your answer.
If the side of a rhombus is and one diagonal is respectively, then the area of the rhombus is .
Write whether the following statement is true or false. Justify your answer.
The area of a regular hexagon of side is the sum of the areas of the five equilateral triangles with side .
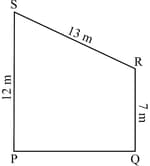
Find the area (in ) of the trapezium with height given in the adjoining figure.
The area of a trapezium is and the height is . Find the lengths of its two parallel sides if one side is greater than the other.
A square and an equilateral triangles have equal perimeters. If a diagonal of the square is , then find the area of the triangle.
The base of an isosceles triangle is and its perimeter is . Find the area of the triangle.
The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is and its base is times of each of its equal sides. Find the length of each side of the triangle, area of the triangle and the height corresponding to its longest side.
