Types of Angles
Important Questions on Types of Angles
In the adjoining figure, bisects . is a ray opposite to ray . Prove that .
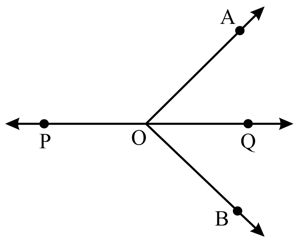
Two adjacent angles are equal. Is it necessary that each of these angles will be a right angle? Justify your answer.
All linear pairs are supplementary angles whereas all supplementary angles are not linear pairs.
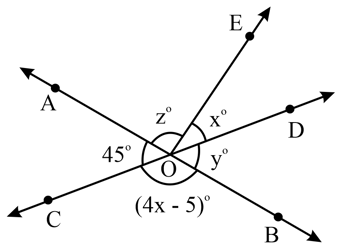
In figure given below, lines and intersect each other at the point . If , find the values of .
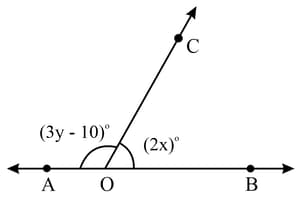
In figure given below, ray stands on line and . Find the measures of and .
The sum of angles at a point on one side of a line is equal to _____ right angles. (one/ two/ three)
In the following figure, and are two straight lines which intersect each other at the point . Find the values of and .
In the following figure, lines and intersect each other at . Find the values of and .
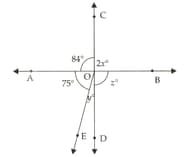
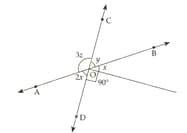
Find the values of and in the following figure:
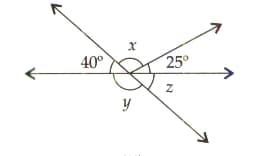
Find the values of and in the following figure:
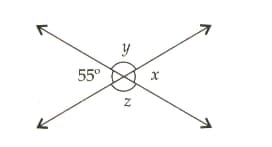
If non-common arms of adjacent angles form a line, then the adjacent angles are said to form _____.
In the adjoining figure, if , then prove that is a straight line.
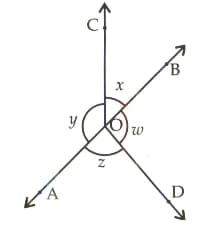
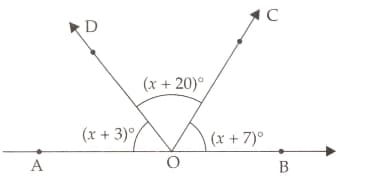
In the adjoining figure, and form a line . If , find the values of and .
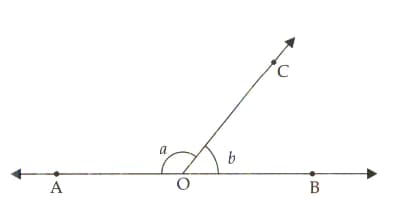
In the adjoining figure, is the bisector of , is the bisector of and . Show that the points and are collinear.
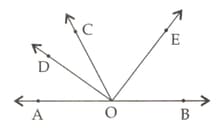
In the adjoining figure, for what value of will a straight line. Justify your answer.
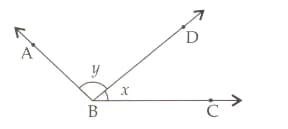
In the adjoining figure, is a straight line. Find the value of .
Two angles measure and . If each angle is the supplement of the other, find the angles.
Find the angle which is one fifth of its complement.
If two lines intersect each other, then the vertically opposite angles are _____. (equal / unequal / different)
The sum of all the angles (drawn at a plane) at a point is _____.

