Human Reproduction Organs
Important Questions on Human Reproduction Organs
The diagram shows a human sperm. Describe how a human egg cell is adapted for its function.

The diagram shows a human sperm. With reference to the diagram, explain how the structure of a sperm adapts it for its function.

The diagram shows a human sperm.

mitochondrion
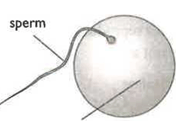
The diagram below shows two gametes: a sperm cell and an egg cell. Suggest an advantage of the egg cell being larger than the sperm cell.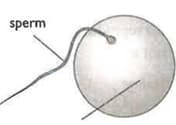
The diagram below shows two gametes: a sperm cell and an egg cell. State one way in which both of these cells differ from other cells of the body.
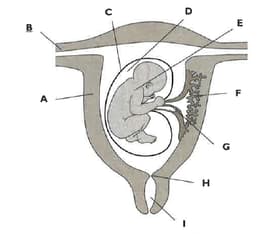
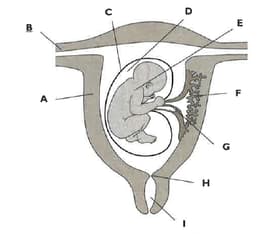
The diagram shows a foetus developing in the uterus.
Outline the function of part F.
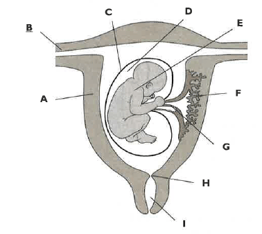
The diagram shows a foetus developing in the uterus.
Describe the function of part C
The diagram shows a foetus developing in the uterus.
Name each of the parts labelled A to I.
Write the name of the parts of the female reproductive system that match the description.
- A ring of muscle at the base of the uterus.
Write the name of the part of the female reproductive system that matches the description.
- The organ in which an embryo develops.
Write the name of the part of the female reproductive system that matches the description.
- The organ where eggs are made.
Write the name of the part of the female reproductive system that matches the description.
- The place where an egg is fertilized.
Copy and complete these sentences about the male reproductive system. You can use each of the words in the list once, more than once or not at all.
Oestrogen, oviducts, primary, progesterone, prostate, secondary, sperm, sperm ducts, testes, testosterone, ureter, urethra.
Sperm are made in the _____ and can travel along with the _____ _____ and then the _____ to the outside world. The _____gland adds fluid to the sperm.
The testes make a hormone called _____ and This causes _____ production to begin, and also causes the development of _____ sexual characteristics.
What is meant by puberty?
List two effects of testosterone.
What is testosterone?
What is meant by adolescence?
What happens if the egg is not fertilised?
Why does the uterus wall become thick and spongy before ovulation?
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of breast-feeding and bottle-feeding.

