Jan Dangerfield, Stuart Haring and, Julian Gilbey Solutions for Exercise 1: CROSS-TOPIC REVIEW EXERCISE 1
Jan Dangerfield Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - Jan Dangerfield, Stuart Haring and, Julian Gilbey Solutions for Exercise 1: CROSS-TOPIC REVIEW EXERCISE 1
Attempt the practice questions from Exercise 1: CROSS-TOPIC REVIEW EXERCISE 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics : Mechanics Course Book solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Jan Dangerfield, Stuart Haring and, Julian Gilbey Solutions for Exercise 1: CROSS-TOPIC REVIEW EXERCISE 1 with Hints & Solutions
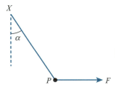
A force acts in a horizontal plane and has components in the -direction and in the -direction relative to a set of axes. The force acts at an angle below the -axis.
Find the sizes of and
The graph shows the velocity of a parachutist as she falls from an aircraft until she hits the ground later.
There are four stages to the motion: falling freely under gravity with the parachute closed; decelerating with the parachute open; falling at constant speed with the parachute open; and coming to rest instantaneously on hitting the ground.
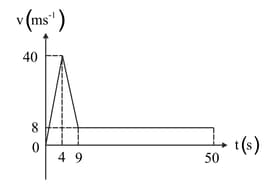
Find the total distance fallen.
The graph shows the velocity of a parachutist as she falls from an aircraft until she hits the ground later.
There are four stages to the motion: falling freely under gravity with the parachute closed; decelerating with the parachute open; falling at constant speed with the parachute open; and coming to rest instantaneously on hitting the ground.
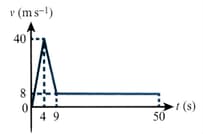
The parachutist has mass Show that the upward force on the parachutist due to the parachute during the second stage is
A particle of mass is attached to one end of a light inextensible string. The other end of the string is attached to a fixed point It is held in equilibrium by a horizontal force when the string is at an angle to the vertical, where Find the tension in the string and the size of
Two forces, each of size have a resultant of
Find the angle between the forces.
Two forces, each of size have a resultant of
The two given forces of magnitude act on a particle of mass which remains at rest on a horizontal surface with no friction. The normal contact force between the surface and the particle has magnitude Find and the acute angle that one of the forces makes with the surface.
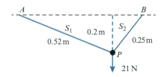
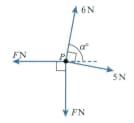
A particle is in equilibrium on a smooth horizontal table under the action of four horizontal forces of magnitudes and acting in the directions shown. Find the values of and
A particle of weight is attached to one end of each of two light inextensible strings, and of lengths and respectively. The other end of is attached to a fixed point and the other end of is attached to a fixed point at the same horizontal level as The particle hangs in equilibrium at a point below the level of with both strings taut (see diagram). Find the tension in and the tension in