Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter, Exercise 16: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Lawrie Ryan Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter, Exercise 16: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: States of Matter, Exercise 16: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook with Digital Access (2 Years) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter, Exercise 16: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
Water and bromine are both simple molecular substances.
When 0.20 g of a liquid, Y, with a simple molecular structure was evaporated it produced 80 cm3 of vapour.
The temperature was 98 °C and the pressure 1.1 × 105 Pa. Calculate the relative molecular mass of Y.
(R = 8.31 JK–1mol–1)
Crystals of sodium chloride have a lattice structure.
Describe a sodium chloride lattice.
Crystals of sodium chloride have a lattice structure.
Explain the following property of sodium chloride:
Sodium chloride has a high melting point.
Crystals of sodium chloride have a lattice structure.
Explain the following property of sodium chloride:
Sodium chloride conducts electricity when molten but not when solid.
Crystals of sodium chloride have a lattice structure.
Explain the following property of sodium chloride:
Sodium chloride is hard but brittle.
The diagram shows some allotropes of carbon.
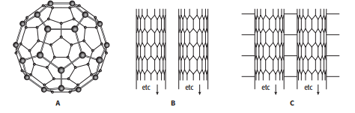
Explain in terms of structure and bonding why structure A is gaseous at 800 °C, but diamond is not.
The diagram shows some allotropes of carbon.
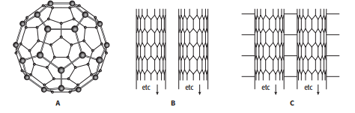
Structure B shows an allotrope of carbon in the form of tubes.
Describe the similarities and differences between structure B and graphite.
The diagram shows some allotropes of carbon.
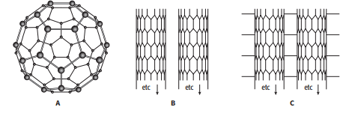
Structure C is stronger than structure B when a force is applied in the same direction as the long axis of the tube.
Explain why structure C is stronger.
