Making Ammonia in Industry
Important Questions on Making Ammonia in Industry
What happens to the unreacted gases in Haber process ?
What is the % yield of ammonia at 200 atmospheres and 450 °C? (Use the graph.)
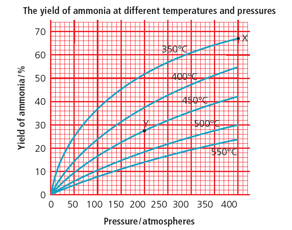
400 atmospheres and 250 °C would give a high yield. Why are these conditions not used in the Haber process?
Explain why high pressure and low temperature help the yield, in making ammonia.
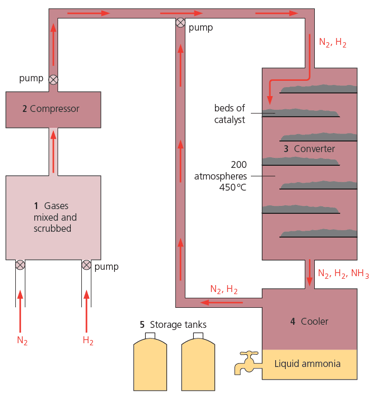
Look at the catalyst beds in the diagram given below. Why are they arranged this way?
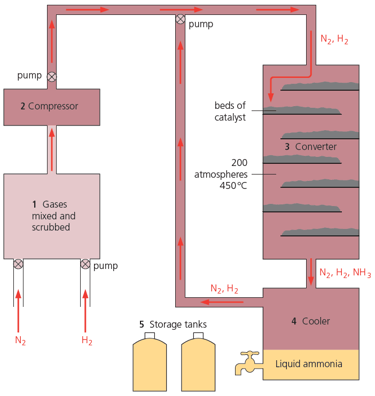
Look at the catalyst beds in the diagram given below. What is in them?
Ammonia is made from nitrogen and hydrogen. Write an equation for the reaction.
Ammonia is made from nitrogen and hydrogen. What is the process for making ammonia called?
Ammonia is made from nitrogen and hydrogen. How are the nitrogen and hydrogen obtained?
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
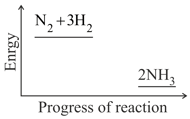
What effect does this catalyst have on the yield of ammonia?
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
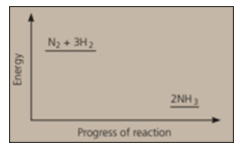
Which catalyst is used in the Haber's process?
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
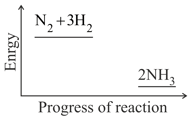
What effect does a catalyst have on an equilibrium reaction?
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
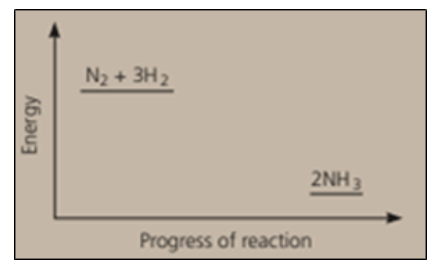
The reaction is reversible, and reaches equilibrium. Explain very clearly what the two terms in italics mean.
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
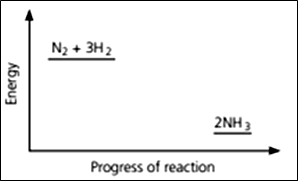
Explain why high temperatures are not used in the manufacture of ammonia.
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.

What does this diagram tell you?
This is about the manufacture of ammonia. In manufacturing ammonia, is the chosen pressure high, low, or moderate? Explain why.
This is about the manufacture of ammonia. What happens to the unreacted nitrogen and hydrogen?
This is about the manufacture of ammonia. Why is the mixture passed over iron?
This is about the manufacture of ammonia. Why are the two gases scrubbed?
This is about the manufacture of ammonia. Which two gases react to give ammonia?
