Capacitors
Important Questions on Capacitors
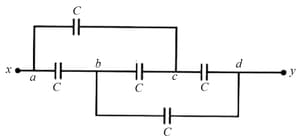
Find equivalent capacitance between and if each capacitor is .
An uncharged capacitor with a solid dielectric is connected to a similar air capacitor charged to a potential of If the common potential after sharing of charges becomes then the dielectric constant of the dielectric must be
Two parallel plate capacitors of capacitances and are connected in parallel and charged to a potential difference The battery is then disconnected and the region between the plates of the capacitor is completely filled with a material of dielectric constant The potential difference across the capacitors now becomes -
A network of resistances, cell and capacitor is shown in adjoining figure. In steady state condition, the charge on capacitor is while is unknown resistance. Values of and are, respectively,
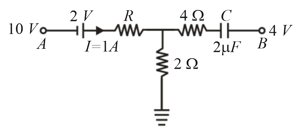
In the given circuit, with steady current, the potential drop across the capacitor must be,
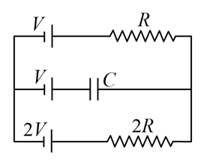
A capacitor of withstands a maximum voltage of while another capacitor of withstands a maximum voltage of . If the two capacitors are connected in series, the system will withstand a maximum voltage of,
A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates is charged to potential difference of and then insulated. A plastic plate is inserted between the plates filling the whole gap. The potential difference between the plates now becomes . The dielectric constant of plastic is,
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with air as dielectric is . If a slab of dielectric constant and of the same thickness as the separation between the plates is introduced so as to fill of the capacitor (shown in figure), then the new capacitance is,

The plates of a parallel plate capacitor are charged up to . A thick dielectric slab is inserted between the plates. Then, to maintain same potential difference, the distance between the capacitor plates is increased by . The dielectric constant of the plate is,
Two capacitors of capacitances and are connected in series and the combination is charged to a potential difference of . If the charge on the combination is , the energy stored in the capacitor of capacity in is,
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with air as the medium is As a dielectric is introduced between the plates, the capacitance becomes The permittivity of the medium in is,
Identical dielectric slabs are inserted into two identical capacitors and These capacitors and a battery are connected as shown in the figure. Now, the slab of capacitor is pulled out with battery remaining connected.
Two identical capacitors have the same capacitance One of them is charged to potential and the other to The negative ends of the capacitors are connected together. When the positive ends are also connected, the decrease in energy of the combined system is,
The plate of a parallel plate capacitor are separated by A plate of thickness with dielectric constant is inserted and the remaining space is filled with a plate of dielectric constant If is the charge on the capacitor and area of plates is each, then the potential difference between the plates is,
Two capacitors of capacities and are connected in parallel and then connected in series with a third capacitor of capacity The combination is charged with volt. The charge on capacitor of capacity is,
The capacity of a capacitor is and its potential is . The energy released on discharging it fully will be
During charging a capacitor, variations of potential of the capacitor with time is shown as,
In the given circuit, initially. Now, a dielectric slab of dielectric constant is inserted in
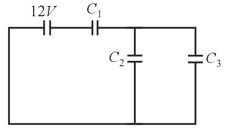
The equivalent capacitance become

