D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Objective Problems [ Level 1 ]
D. C. Pandey Physics Solutions for Exercise - D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Objective Problems [ Level 1 ]
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 2: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Objective Problems [ Level 1 ] with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Complete Study Pack for Engineering Entrances Objective Physics Vol 2 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Objective Problems [ Level 1 ] with Hints & Solutions
Consider four circuits shown in the figure below. In which circuit power dissipated is greatest? (Neglect the internal resistance of the power supply)
The terminal potential difference of a cell is greater than its emf when it is
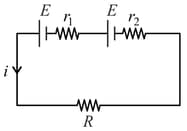
The internal resistances of two cells shown are and . If , the potential difference across the cell
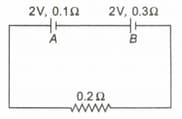
How much work is required to carry a charge from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a battery?
The rows each containing cells in series are joined in parallel. Maximum current is taken from this combination across an external resistance of resistance. If the total number of cells used are and internal resistance of each cell is then
If is the of a cell of internal resistance and external resistance , then potential difference across is given as
When cells are joined in parallel combination as shown, the strength of the current is given by
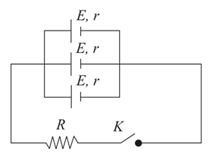
Two cells of the same EMF but different internal resistances and are connected in series with an external resistance as shown in the figure. The terminal potential difference across, the second cell is found to be zero. The external resistance must then be: