David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Work and Power, Exercise 5: End-of-chapter questions
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Work and Power, Exercise 5: End-of-chapter questions
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Work and Power, Exercise 5: End-of-chapter questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge IGCSE® Physics Coursebook Second Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang Solutions for Chapter: Work and Power, Exercise 5: End-of-chapter questions with Hints & Solutions
Two geologists are collecting rocks from the bottom of a cliff. The rocks are located into a basket and then pulled up the cliff on the end of rope, as shown in the diagram.
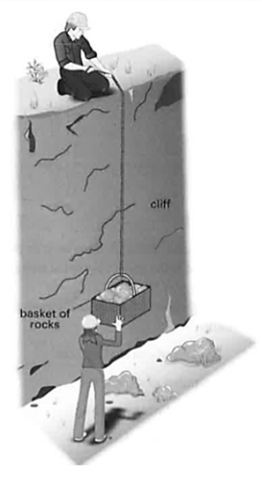
The basket of rocks is brought to rest at the top of the cliff.
Which form of energy that the basket possess is significantly greater at the top of the cliff than when it is at the bottom of the cliff?
Two geologists are collecting rocks from the bottom of a cliff. The rocks are located into a basket and then pulled up the cliff on the end of rope, as shown in the diagram.
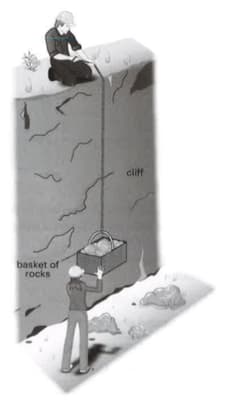
The basket of rocks is brought to rest at the top of the cliff.
Which two measurements must be made in order to calculate the increase in energy in it?
Two geologists are collecting rocks from the bottom of a cliff. The rocks are located into a basket and then pulled up the cliff on the end of rope, as shown in the diagram.
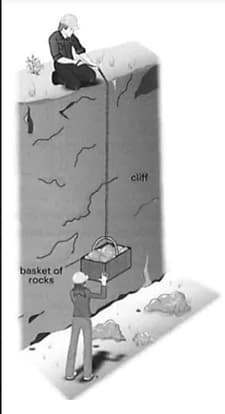
The basket of rocks is brought to rest at the top of the cliff. Which form of energy in his body has the man at the top of the cliff used in order to raise the basket of rocks?
Two geologists are collecting rocks from the bottom of a cliff. The rocks are located into a basket and then pulled up the cliff on the end of rope, as shown in the diagram.
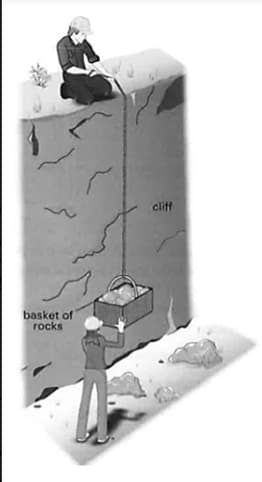
The basket of rocks is brought to rest at the top of the cliff.
State the measurement needed, in order to calculate the useful power developed by the man at the top of the cliff.
An ornamental garden includes a small pond, which contains a pumped system that causes water to go up a pipe and then to run down a heap of rocks.
The diagram shows a section through this water feature.
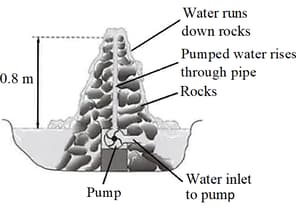
The density of water is . A volume of litre of water is equal to .
Calculate the mass of litre of water.
An ornamental garden includes a small pond, which contains a pumped system that causes water to go up a pipe and then to run down a heap of rocks.
The diagram shows a section through this water feature.
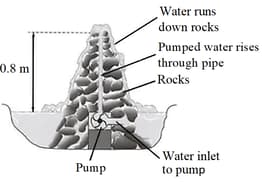
The density of water is . A volume of litre is equal to . Assume .
Calculate the work done raising litre of water through a height of .
An ornamental garden includes a small pond, which contains a pumped system that causes water to go up a pipe and then to run down a heap of rocks.
The diagram shows a section through this water feature.
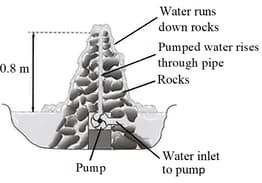
The density of water is . A volume of is equal to . Assume
The pump lifts of water per minute. Calculate the minimum power of the pump.
An ornamental garden includes a small pond, which contains a pumped system that causes water to go up a pipe and then to run down a heap of rocks.
The diagram shows a section through this water feature.
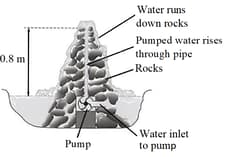
The density of water is . A volume of litre is equal to . Assume .
The pump is switched off. Immediately after the pump is switched off, what is the value of the water pressure at the bottom of the pipe, due to the water in the pipe?
