David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics: Describing Motion, Exercise 14: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics: Describing Motion, Exercise 14: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 1: Kinematics: Describing Motion, Exercise 14: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics: Describing Motion, Exercise 14: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
A student drops a small black sphere alongside a vertical scale

A student drops a small black sphere alongside a vertical scale marked in centimetres. A number of flash photographs of the sphere are taken at intervals, The diagram is shown sideways-the first black dot is a and the next at
. The first photograph is taken with the sphere at the top at the time .
Determine the constant speed reached by the sphere.
A student drops a small black sphere alongside a vertical scale

A student drops a small black sphere alongside a vertical scale marked in centimetres. A number of flash photographs of the sphere are taken at intervals,The diagram is shown sideways-the first black dot is a and the next at .The first photograph is taken with the sphere at the top at the time .
Determine the distance that the sphere has fallen when
A student drops a small black sphere alongside a vertical scale
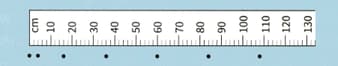
A student drops a small black sphere alongside a vertical scale marked in centimetres. A number of flash photographs of the sphere are taken at intervals,The diagram is shown sideways-the first black dot is a and the next at .The first photograph is taken with the sphere at the top at the time .
In a real photograph, each image of the sphere appears slightly blurred, because each flash is not instantaneous and takes a time of . Determine the absolute uncertainty that this gives in a position of the black sphere when it is travelling at a final constant speed.
Suggest whether this should be observable on the diagram.
State one difference between a scalar quantity and a vector quantity and give an example of each.
A Plane has an airspeed of due north. A Wind blows at from east to west. Draw a vector diagram to calculate the resultant velocity of the plan Give The direction of travel of the plane with respect to north.
A Plane has an airspeed of due north. A Wind blows at from east to west. Draw a vector diagram to
The plane lies for . Calculate the displacement of the plane in this time.
A small aircraft for one is used for a short horizontal flight. On its journey from , the resultant velocity is in a direction east of north and the wind velocity is due north. Show that for the aircraft to travel from it should point due east.
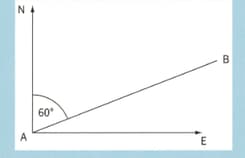
A small aircraft for one is used for a short horizontal flight. On its journey from , the resultant velocity is in a direction east of north and the wind velocity is due north.
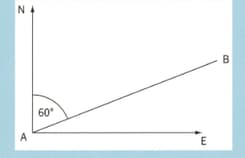
After flying from , the aircraft return along the same path from with a resultant velocity of assuming that the time spent at is negligible, calculate the average speed for the complete journey from and back to .
