David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Matter and Materials, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Matter and Materials, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Matter and Materials, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Matter and Materials, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
A boy stands on a platform of area and a manometer measures the pressure created in a flexible plastic container by the weight of the boy, as shown.
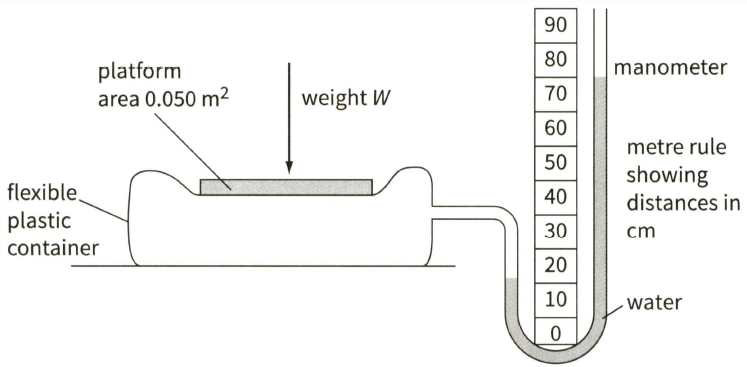
The density of water is . Determine the weight of the boy.
The diagram shows water in a container filled to a depth of . The density of water is .
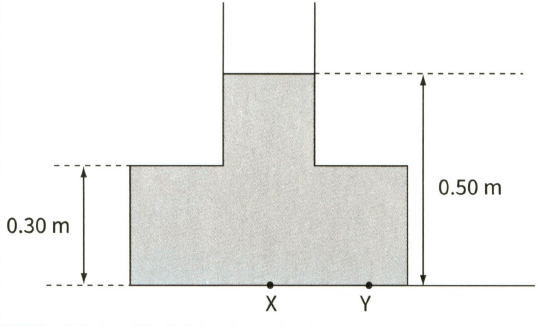
Calculate the pressure at X on the base of the container.
This diagram shows water in a container filled to a depth of . The density of water is .
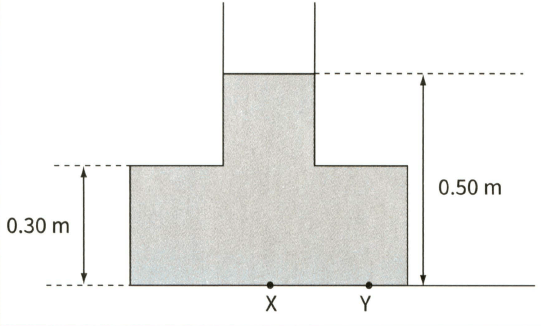
Explain why the pressure at X must be equal to the pressure at Y.
This diagram shows water in a container filled to a depth of . The density of water is .

(c) Explain why the force downwards on the base of the container is larger than the weight of the liquid in the container.
A light spring that obeys Hooke's law has an unstretched length of . When an object of mass is hung from the spring the length of the spring becomes . When the object is fully submerged in a liquid of density , the length of the spring becomes . Calculate the spring constant of the spring.
A light spring that obeys Hooke's law has an unstretched length of . When an object of mass is hung from the spring the length of the spring becomes . When the object is fully submerged in a liquid of density , the length of the spring becomes . Calculate the upthrust on the object.
A light spring that obeys Hooke's law has an unstretched length of . When an object of mass is hung from the spring the length of the spring becomes . When the object is fully submerged in a liquid of density , the length of the spring becomes . Calculate the volume of the object.
A light spring that obeys Hooke's law has an unstretched length of . When an object of mass is hung from the spring the length of the spring becomes . When the object is fully submerged in a liquid of density , the length of the spring becomes . Calculate the density of the material from which the object is made.
