David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Momentum, Exercise 5: Questions
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Momentum, Exercise 5: Questions
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 6: Momentum, Exercise 5: Questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Momentum, Exercise 5: Questions with Hints & Solutions
Figure shows two identical balls A and B about to make a head-on collision. After the collision, ball A rebound at a speed of And ball B rebounds at a speed of . The mass of each ball is .
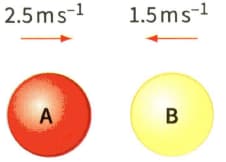
(a) Calculate the momentum of each ball before the collision.
Figure shows two identical balls A and B about to make a head-on collision. After the collision, ball A rebound at a speed of And ball B rebounds at a speed of . The mass of each ball is .
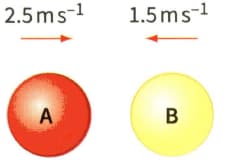
(b) Calculate the momentum of each ball after the collision.
Figure shows two identical balls A and B about to make a head-on collision. After the collision, ball A rebound at a speed of And ball B rebounds at a speed of . The mass of each ball is .
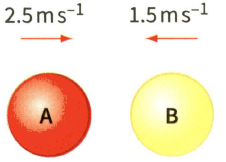
(c) Is the momentum conserved in the collision?
Figure shows two identical balls A and B about to make a head-on collision. After the collision, ball A rebound at a speed of And ball B rebounds at a speed of . The mass of each ball is .
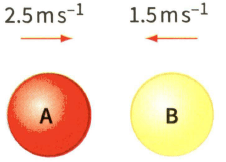
(d) Show that the total kinetic energy of the two balls is conserved in the collision.
Figure shows two identical balls A and B about to make a head-on collision. After the collision, ball A rebound at a speed of And ball B rebounds at a speed of . The mass of each ball is .
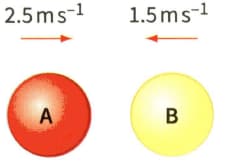
(e) Show that the relative speed of the balls is the same before and after the collision.
A trolley of mass is moving at . It collides with a stationary trolley of mass . This second trolley moves off at .
(a) Draw 'before' and 'after' diagrams to show the situation.
A trolley of mass is moving at . It collides with a stationary trolley of mass . This second trolley moves off at .
(b) Use the principle of conservation of momentum to calculate the speed of the first trolley after the collision. In what direction does it move?
