David Weber, Talei Kunkel, Alexander Martinez and, Rebecca Shultis Solutions for Chapter: Probability Games and Play, Exercise 22: Practice 5
David Weber Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - David Weber, Talei Kunkel, Alexander Martinez and, Rebecca Shultis Solutions for Chapter: Probability Games and Play, Exercise 22: Practice 5
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Probability Games and Play, Exercise 22: Practice 5 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MYP Mathematics A concept-based approach 2 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Weber, Talei Kunkel, Alexander Martinez and, Rebecca Shultis Solutions for Chapter: Probability Games and Play, Exercise 22: Practice 5 with Hints & Solutions
A six-sided die is rolled times. If the die lands with a or facing up, the player wins.If the die lands on the player loses. Consider the table of collected data
| Number rolled | Frequency |
Find the experimental probability of winning and losing.
A six-sided die is rolled times. If the die lands with a or facings up, the player wins. If the die lands on or , the player loses. Consider the table of collected data.
| Number rolled | Frequency |
What is the theoretical probability of winning? What is the theoretical probability of losing?
A six-sided die is rolled times. If the die lands with a or facings up, the player wins. If the die lands on , , or , the player loses. Consider the table of collected data.
| Number rolled | Frequency |
Are you surprised by the result of experimental and theoretical probability of winning? Explain.
A spinner with three equal sections was spun times.The results are as shown:
| score | |||
| frequency |
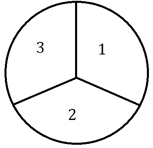
Compare the value to the theoretical probability.
A spinner with three equal sections was spun times. The results are as shown :
| Score | |||
| Frequency |
Find the theoretical and experimental probability of spinning . Represent the experimental probability as a decimal.
A spinner with three equal sections was spun times. The results are as shown:
| score | |||
| frequency |
What would you expect to happen to the experimental probability of spinning if you were to spin the spinner times or more? Explain.
An sided die is rolled, and a coin is tossed. Make a tree diagram of sample space to find the probability of getting a head and an odd number.
Give an example of a method to simulate the outcomes of choosing one pair of jeans from a group of four pairs which are equally popular.