Dean Chalmers and Julian Gilbey Solutions for Chapter: Probability, Exercise 2: EXERCISE 4A
Dean Chalmers Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - Dean Chalmers and Julian Gilbey Solutions for Chapter: Probability, Exercise 2: EXERCISE 4A
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Probability, Exercise 2: EXERCISE 4A with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics : Probability & Statistics 1 Course Book solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Dean Chalmers and Julian Gilbey Solutions for Chapter: Probability, Exercise 2: EXERCISE 4A with Hints & Solutions
Katya randomly picks one of the cards shown.
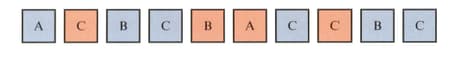
If she repeats this times, how many times is Katya expected to pick a card that is not blue and does not have a letter on it?
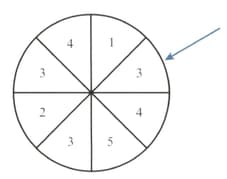
A numbered wheel is divided into eight sectors of equal size, as shown. The wheel is spun until it stops with the arrow pointing at one of the numbers.
Axel decides to spin the wheel times.
Find the number of times the arrow is not expected to point at a
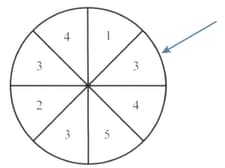
A numbered wheel is divided into eight sectors of equal size, as shown. The wheel is spun until it stops with the arrow pointing at one of the numbers.
Axel decides to spin the wheel times.
How many more times must Axel spin the wheel so that the expected number of times that the arrow points at a is at least ?
A bag contains black and white counters, and the probability of selecting a black counter is .
What is the smallest possible number of white counters in the bag?
A bag contains black and white counters, and the probability of selecting a black counter is .
Without replacement, three counters are taken from the bag and they are all black. What is the smallest possible number of white counters in the bag?
When a coin is randomly selected from a savings box, each coin has a chance of not being selected. How many coins are in the savings box?
A set of data values is and . Find the probability that a randomly selected value is more than one standard deviation from the mean.
One student is randomly selected from a school that has boys. The probability that a girl is selected is . Find the probability that a particular boy is selected.
