Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams
Important Questions on Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams
For three low density gases pressure versus temperature graphs are plotted while keeping them at constant volume, as shown in the figure
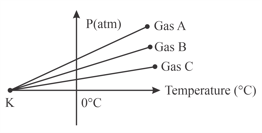
The temperature corresponding to the point is:
A sample of gas at temperature is adiabatically expanded to double its volume. The work done by the gas in the process is given, (given ) :
Heat energy of is given to a diatomic gas allowing the gas to expand at constant pressure. Each gas molecule rotates around an internal axis but do not oscillate. The increase in the internal energy of the gas will be:
The correct relation between and temperature is :
In an Isothermal change, the change in pressure and volume of a gas can be represented for three different temperature; as:
According to law of equipartition of energy the molar specific heat of a diatomic gas at constant volume where the molecule has one additional vibrational mode is :-
Let be the ratio of molar specific heat at constant pressure and molar specific heat at constant volume of a monoatomic gas and be the similar ratio of diatomic gas. Considering the diatomic gas molecule as a rigid rotator, the ratio is:
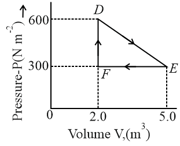
A thermodynamic system is taken from an original state to an intermediate state by the linear process shown in the figure. Its volume is then reduced to the original volume from to by an isobaric process. The total work done by the gas from to to will be
One mole of a monoatomic gas is mixed with three moles of a diatomic gas. The molecular specific heat of mixture at constant volume is ; then the value of will be _____ . (Assume that the given diatomic gas has no vibrational mode.)
At a certain temperature, the degrees of freedom per molecule for gas is . The gas performs of work when it expands under constant pressure. The amount of heat absorbed by the gas will be _____ .
mole of certain monoatomic ideal gas undergoes a temperature increase of at constant pressure. The increase in the internal energy of the gas in this process is
(Given )
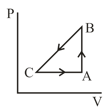
A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process as shown in figure. It absorbs, of heat during the part , no heat during and rejects of heat during . A work of is done on the gas during the part . The internal energy of the gas at is . The work done by the gas during the part is
The total internal energy of two mole monoatomic ideal gas at temperature will be _____ . (Given )
Statement - I : When amount of an ideal gas undergoes adiabatic change from state to state , then work done is , where and universal gas constant.
Statement - II : In the above case, when work is done on the gas, the temperature of the gas would rise.
A diatomic gas does of work when it is expanded isobarically. The heat given to the gas in the process is _____ .
A thermally insulated vessel contains an ideal gas of molecular mass and ratio of specific heats . Vessel is moving with speed and is suddenly brought to rest. Assuming no heat is lost to the surrounding and vessel temperature of the gas increases by :
( universal gas constant)
The ratio of specific heats in terms of degree of freedom is given by :
A monoatomic gas performs a work of , where is the heat supplied to it. The molar heat capacity of the gas will be _____ during this transformation, where is the gas constant.
Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from volume to in three different ways. The work done by the gas is if the process is purely isothermal, , if the process is purely adiabatic and if the process is purely isobaric. Then, choose the correct option
A sample of gas with is taken through an adiabatic process in which the volume is compressed from to If the initial pressure is The absolute value of the work done by the gas in the process

