Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: cbse-2018
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: cbse-2018
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: cbse-2018 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR PHYSICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: cbse-2018 with Hints & Solutions
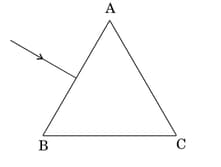
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having a refractive index , placed in water of refractive index . Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
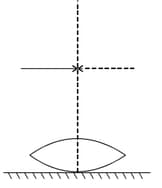
A symmetric biconvex lens of the radius of curvature and made of glass of refractive index , is placed on a layer of liquid placed on top of a plane mirror as shown in the figure. An optical needle with its tip on the principal axis of the lens is moved along the axis until its real, inverted image coincides with the needle itself. The distance of the needle from the lens is measured to be . On removing the liquid layer and repeating the experiment, the distance is found to be . Obtain the expression for the refractive index of the liquid in terms of and .
Draw a labelled ray diagram of an astronomical telescope in the near point adjustment position.
A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length and an eyepiece of focal length . If this telescope is used to view the Moon, find the diameter of the image of the Moon formed by the objective lens. The diameter of the Moon is , and the radius of the lunar orbit is .
Under what conditions is the phenomenon of total internal reflection of light observed? Obtain the relation between the critical angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium.
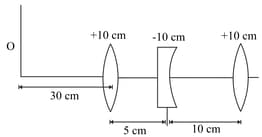
Three lenses of focal length are arranged coaxially as in the figure given below. Find the position of the final image formed by the combination.
Using lens maker’s formula, derive the thin lens formula for a biconvex lens.
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror. It is observed that a virtual image is formed. Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation and hence derive the mirror equation .
An object is placed in front of a plano-convex lens with its spherical surface of radius of curvature . If the refractive index of the material of the lens is , find the position and nature of the image formed.
