Reactivity of Metals
Reactivity of Metals: Overview
This topic covers the reactivity series of metals. It also discusses why and how metals and non-metals react. You will learn about the most and least reactive metals along with combination of atoms and Lewis structure.
Important Questions on Reactivity of Metals
Which of the following reactions will not proceed?
Rashmi added aluminum metal to colourless solution of zinc sulphate. After half an hour, the solution was observed. It was colourless.
She recorded her observations in the following statements:
(i) No reaction occurred
(ii) Reaction occurred and aluminium sulphate was formed
(iii) Zinc is more reactive than aluminium
(iv) Aluminium is more reactive than zinc.
The correct observations are:
Raman took three metals labelled and . He carried out displacement reactions with his salt solutions and found that is less reactive than but more reactive than . The metals and respectively could be:
A chemistry lab-incharge kept zinc metal in solution and observed that after sometime, green ferrous sulphate solution turns to colourless and some brown powder is deposited on zinc. In the above reaction, zinc metal acts as:
Madhurima added a few iron filings to of aluminium sulphate solution in a test tube. The correct observation for change in colour of solution by her is:
Rekha took two solutions, each separately in two test tubes A and B. The solutions were of and , respectively. The colours of the two solutions were:
Rinku took each of two solutions and separately in two test tubes. The solutions were copper sulphate and zinc sulphate respectively. The colours of the two solutions were:
An iron nail is suspended in copper sulphate solution and kept for a while. It is observed that the solution:
A student performed the following four experiments.
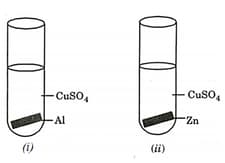
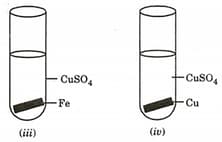
The experiments in which solid deposition on the metal plate will be observed are:
The aqueous solutions of copper sulphate and zinc sulphate appear
A thin plate of zinc metal is placed in a beaker containing aqueous ferrous sulphate solution. The zinc plate is taken out after mins. The colour of solution changes to:
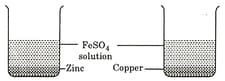
Two beakers A and B contain an aqueous solution of FeSO4. In the beaker A, zinc granules and in beaker B copper turnings have been placed. A grey coating was observed on zinc but not on copper. From the above observations, we can conclude.
Solutions of copper sulphate, iron sulphate and zinc sulphate are prepared and marked and respectively. Few pieces of aluminium are added to each solution. After some time a change will be observed in:
Zinc granules are placed in each of the four solutions and as shown. Colour change would be observed in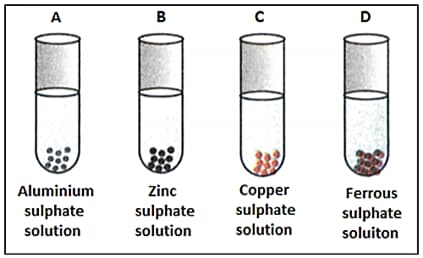
Two beakers and contain iron sulphate solution. In breaker , a small piece of copper and in beaker a small piece of zinc are placed. It is found that after some time a grey deposit forms on zinc but not on copper. From these observations it can be concluded that:
Copper on exposure to air, gets a green coating due to formation of:
Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating a layer of:
In amalgam, a metal is dissolved in:
During electrolytic refining of metal, metal:
Metal refined by electrolytic process is:
