Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 28: Alternating Current, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
A coil has an inductance of and is joined in series with a resistance of When an alternating e.m.f. of at c.p.s. is applied to it, then the watt-less component of the RMS current in the circuit is
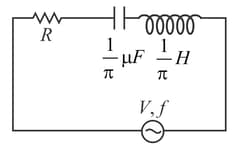
A circuit is set up by connecting in series. An alternating emf of is applied across this series combination. Which of the following is correct.
In a series circuit with an source (peak voltage ), Then
In the circuit shown below, the supply voltage has constant rms value but variable frequency . At resonance, the circuit
A town situated away from a power house at requires of electric power at. The resistance of transmission line carrying power is . The town gets power from the line through a step-down transformer at a substation in the town. Which of the following is/are correct
of electric power can be transmitted to a distant station at (i) or (ii) Which of the following is correct.
Power factor may be equal to for :
In a series circuit, the supply voltage is kept constant at and the frequency of the sinusoidal voltage is varied from . The voltage across the resistance is measured each time as . For the determination of the , a student wants to draw a linear graph and try to get from the slope. Then she may draw a graph of
