Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Kinematics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
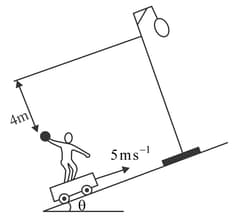
A man is travelling on a flat car which is moving up a plane inclined at to the horizontal with a speed . He throws a ball towards a stationary hoop located perpendicular to the incline in such a way that the ball moves parallel to the slope of the incline while going through the centre of the hoop. The centre of the hoop is high from the man's hand calculate the time taken (in ) by the ball to reach the hoop in second.
A stone is projected horizontally with speed from a height above ground. A horizontal wind is blowing in a direction opposite to the velocity of projection and gives the stone a constant horizontal acceleration (in a direction opposite to the initial velocity). As a result, the stone falls on the ground at a point vertically below the point of projection. Then find the value of .
( is acceleration due to gravity)
If at an instant the velocity of a projectile be and its inclination to the horizontal be at what time interval (in ) after that instant will the particle be moving at right angles to its former direction.
An open tank long and deep, is filled up to a height of oil of specific gravity The tank is accelerated uniformly from rest to a speed of . The shortest time (in seconds) in which this speed may be attained without spilling any oil (in sec).
A stone is projected from level ground at such that its horizontal and vertical components of initial velocity are and , respectively. Then the instant of time at which magnitude of tangential and magnitude of normal components of acceleration of stone are same is (neglect air resistance). (Use ).
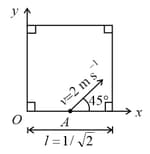
A striker is shot from a square carom board from a point A exactly at midpoint of one of the walls with a speed at an angle of with the as shown. The collisions of the striker with the walls of the fixed carom are perfectly elastic. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the striker and board is
In the figure shown all the surface are smooth. All the blocks and are movable -axis is horizontal and y-axis vertical as shown. Just after the system is released from the position as shown.
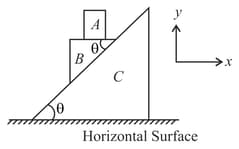
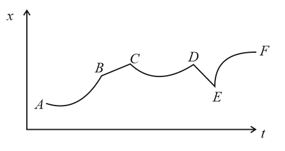
Figure shows the displacement of a particle going along the -axis as a function of time. Find the region where force acting on the particle is zero.