Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 18: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
The volume thermal expansion coefficient of an ideal gas at constant pressure is
(Here absolute temperature of gas)
Two identical rooms in a house are connected by an open doorway. The temperatures in the two rooms are maintained at two different values. Therefore,
Two moles of hydrogen are mixed with moles of helium. The root-mean-square speed of gas molecules in the mixture is times the speed of sound in the mixture. Then, is,
Consider a collision between an argon molecule and a nitrogen molecule in a mixture of argon and nitrogen kept at room temperature. Which of the following are possible?
An ideal gas of one mole is kept in a rigid container of negligible heat capacity. If of heat is supplied, the gas temperature raises by . Then, the gas may be,
Graph shows a hypothetical speed distribution for a sample of gas particle .
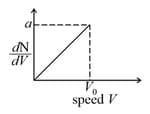
The following sets of values for and of an ideal gas have been reported by different students. The units are . Which of these sets is most reliable ?
Let and moles of two different ideal gases be mixed. If adiabatic coefficient of the two gases are and , respectively, then adiabatic coefficient of the mixture is given through the relation
