Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Sound Waves, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Sound Waves, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 21: Sound Waves, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Sound Waves, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
The ratio of speeds of sound in nitrogen gas to that in helium gas at is
A closed pipe and an open pipe have their first overtones identical in frequency. Their lengths are in the ratio
A source of sonic oscillations with frequency and a receiver are located on the same normal to a wall. Both the source and the receiver are stationary, and the wall recedes from the source with velocity . Find the beat frequency registered by the receiver. The velocity of sound is equal to .
Two narrow organ pipes, one open and the other closedare sounded in their respective fundamental modes. The beat frequency heard is If now the pipes are sounded in their first overtones, then also the beat frequency heard is Then:
Select all the correct alternatives. Two identical straight wires are stretched so as to produce when vibrating simultaneously. On changing the tension slightly in one of them, the beat-frequency remains unchanged. Denoting by the higher and the lower initial tensions in the strings, then it could be said that while making the above changes in tension.
A girl stops singing a pure note. She is surprised to hear an echo of higher frequency, i.e., a higher musical pitch. Then:
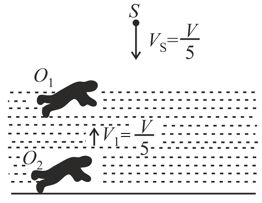
In the figure shown an observer floats (static) on the water surface with ears in air while another observer is moving upwards with constant velocity in water. The source moves down with constant velocity and emits the sound of frequency . The velocity of sound in air is and that in water is For the situation shown in figure:
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitude of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double that of the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the two wave be and their displacement amplitudes be , then
