Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4 with Hints & Solutions
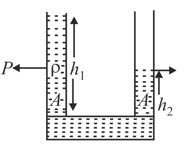
Two identical cylindrical vessels with their bases at the same level each contain a liquid of density as shown in the figure. The height of the liquid in one vessel is and in other vessels , the area of either base is . Find the work done by gravity in equalizing the levels when the two vessels are connected.
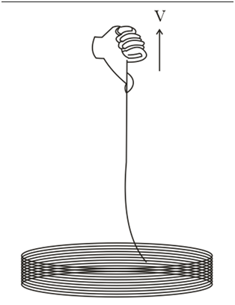
A uniform rope of linear mass density and length is coiled on a smooth horizontal surface. One end is pulled up with constant velocity Then find average power applied by the external agent in pulling the entire rope just off the ground ?
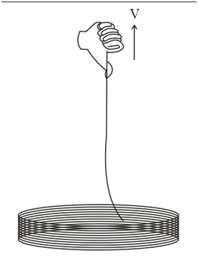
A uniform rope of linear mass density and length is coiled on a smooth horizontal surface. One end is pulled up with a constant velocity . The maximum power delivered by the agent in pulling up the rope is?
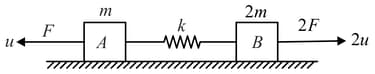
Two blocks of mass respectively are joined to the ends of an undeformed massless spring of spring constant . They can move on a horizontal smooth surface. Initially have velocities towards left and towards right respectively. Constant forces of magnitudes are always acting on respectively in the directions shown. Find the maximum extension in the spring during the motion.
A chain of mass and length is held vertically such that its bottom end just touches the surface of a horizontal table. The chain is released from rest. Assume that the portion of chain on the table does not form a heap, the momentum of the portion of the chain above the table after the top end of the chain falls down by a distance ,
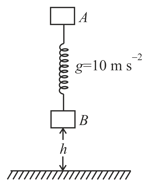
From what minimum height in metre must the system be released when the spring is in its natural length as shown in the figure so that after a perfectly inelastic collision of block with ground, may be lifted off ground.
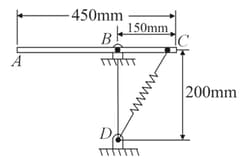
A uniform rod rotates in a vertical plane about a smooth pivot at . A spring of constant and of unstretched length is attached to the rod as shown. Knowing that in the position shown the rod has an angular velocity of clockwise, determine the angular velocity of the rod after it has rotated through.
(a) (b)
A carpet of mass made of inextensible material is rolled along its length in the form of a cylinder of radius and is kept on a rough floor. The carpet starts unrolling without sliding on the floor when a negligibly small push is given to it. Calculate the horizontal velocity of the axis of the cylindrical part of the carpet when its radius reduces to .