Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
A light rod of length I has two masses and attached to its two ends. The moment of inertia of the system about an axis perpendicular to the rod and passing through the centre of mass is
A body of mass is lying in . plane at rest. It suddenly explodes into three pieces. Two pieces, each of mass move perpendicular to each other with equal speeds . The total kinetic energy generated due to explosion is
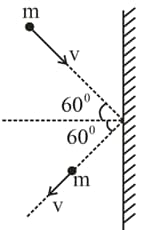
A rigid ball of mass strikes a rigid wall at and gets reflected without loss of speed as shown in the figure below. The value of impulse imparted by the wall in the ball will be
Two identical balls and having velocities of and respectively collide elastically in one dimension. The velocities of and after the collision respectively will be
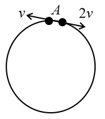
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities fare and , respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collisions, the particles move at constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at , these two particles will again reach the point
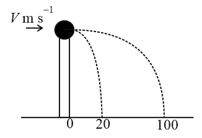
A ball of mass rests on a vertical post of height . A bullet of mass , travelling with a velocity in a horizontal direction, hits the centre of the ball. After the collision, the ball and bullet travel independently. The ball hits the ground at a distance of and the bullet at a distance of from the foot of the post. The initial velocity of the bullet is
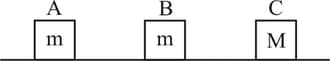
Three blocks and are lying on a smooth horizontal surface, as shown in the figure. and have equal masses, and has mass . Block is given an initial speed towards due to which it collides with perfectly inelastically. The combined mass collides with , also perfectly inelastically. of the initial kinetic energy is lost in the whole process. What is value of ?
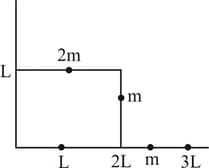
The position vector of the centre of mass of an asymmetric uniform bar of a negligible area of cross-section, as shown in the figure is: