Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Circular Motion, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with Hints & Solutions
A particle of mass is moving with constant velocity on smooth horizontal surface. A constant force starts acting on particle perpendicular to velocity . Radius of curvature after force start acting is:
A car moving on a horizontal road may be thrown out of the road in taking a turn
If angular displacement of a particle moving on a curved path be given as, where is in sec, the angular velocity at will be
A wheel starts rotating from rest with constant and attains an angular velocity of in . The total angular displacement in radians will be
A fan is running at It is switched off. It comes to rest by uniformly decreasing its angular speed in . The total number of rotations in this period.
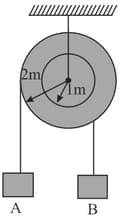
In the pulley system (stick to each other) shown, if radii of the bigger and smaller pulley are and respectively and the acceleration of block is in the downward direction, then the acceleration of block will be:
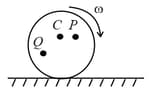
is the point of contact between a wheel and the ground. The radius of the wheel is . The wheel rolls on the ground without slipping. The displacement of point , when the wheel completes half rotation is
A disc is moving without slipping on ground then the relation between magnitude of velocity of points , and is [distance ]