Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 13: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
A wind with speed blows parallel to the roof of a house. The area of the roof is . Assuming that the pressure inside the house is atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the wind on the roof and the direction of the force will be
The cylindrical tube of a spray pump has radius , one end of which has fine holes, each of radius . If the speed of the liquid in the tube is , the speed of ejection of the liquid through the holes is,
Two non-mixing liquids of densities and are put in a container. The height of each liquid is . A solid cylinder of length and density is put in this container. The cylinder floats with its axis vertical and length in the denser liquid. The density is equal to:
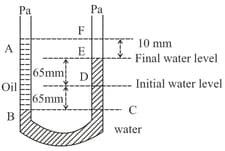
A tube with both ends open to the atmosphere is partially filled with water. Oil; which is immiscible with water, is poured into one side until it stands at a distance of above the water level on the other side. Meanwhile, the water rises by from its original level (see diagram). The density of the oil is:
A small hole of area cross-section is present near the bottom of a fully filled open tank of height Taking , the rate of flow of water through the open hole would be nearly
Water is flowing continuously from a tap having an internal diameter of . The water velocity as it leaves the tap is . The diameter of the water stream at a distance below the tap, is close to
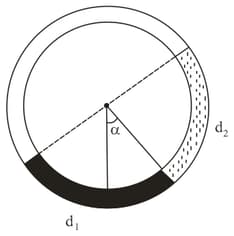
There is a circular tube in a vertical plane. Two liquids that do not mix and of densities and are filled in the tube. Each liquid subtends angle at the centre. Radius joining their interface makes an angle with vertical. Ratio is:
A load of mass is suspended from a steel wire of length and radius in Searle's apparatus experiment. The increase in length produced in the wire is Now the load is fully immersed in a liquid of relative density The relative density of the material of load is The new value of the increase in length of the steel wire is -
