Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Friction, Exercise 4: Exercise-4
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Friction, Exercise 4: Exercise-4
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Friction, Exercise 4: Exercise-4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Friction, Exercise 4: Exercise-4 with Hints & Solutions
The upper portion of an inclined plane of inclination is smooth and the lower portion is rough. A particle slides down from the top and just comes to rest at the foot. If the ratio of the smooth length to rough length is then the coefficient of friction is:
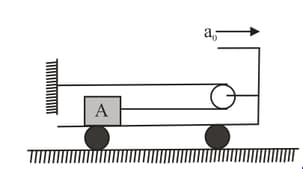
Starting from rest, a flat car is given a constant acceleration, . A cable is connected to a crate of mass as shown. Neglect the friction between the floor and car wheels and mass of pulley. Calculate the corresponding tension in the cable. The coefficient of friction between crate and floor of the car is . The tension in cable is,
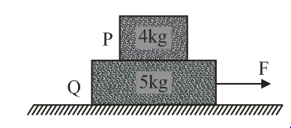
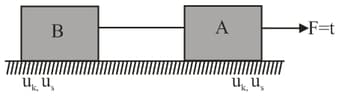
The coefficient of friction between and blocks is and between block and ground is , respectively. Choose the correct statements.
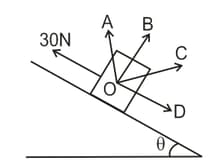
A body of mass lies on a rough inclined plane of inclination with the horizontal. When a force of is applied on the block parallel to and upward the plane, the total reaction by the plane on the block is nearly along:
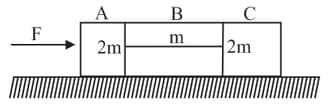
The system is pushed by a force as shown in figure. All surfaces are smooth except between and . The friction coefficient between and is . The minimum value of to prevent block from downward slipping is,
A force is applied to a block as shown in figure where is time in seconds. The force is applied at when the system was at rest. Which of the following graph correctly gives the frictional force between and horizontal surface as a function of time . Assume that at , the tension in the string connecting the two blocks is zero.
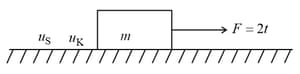
A force (where is the time, in seconds). The force is applied at to the block of mass placed on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of static and kinetic friction between the block and surface are and , respectively. Which of the following graphs best represents the acceleration vs time of the block .
A block lying on a long horizontal conveyor belt moving at a constant velocity receives a velocity (relative to the ground) in the direction opposite to the direction of motion of the conveyor. After the velocity of the block becomes equal to the velocity of the belt. The coefficient of friction between the block and the belt is The magnitude of velocity of the conveyor belt is (Use ) :
