Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 18: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with Hints & Solutions
An ideal gas is initially at temperature and volume Its volume is increased by due to an increase in temperature pressure remaining constant. The quantity varies with temperature as:
Which of the following graphs correctly represents the variation of with for an ideal gas at constant temperature?
One mole of a monatomic ideal gas is taken along two cyclic processes and as shown in the diagram. The processes involved are purely isochoric, isobaric, isothermal or adiabatic.
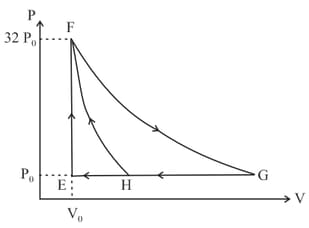
Match the paths in List I with the magnitudes of the work done in List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
Assertion: The root mean square velocity of molecules of a gas having Maxwellian distribution of velocities is higher than their most probable velocity at any temperature.
Reason: A very small number of molecules of a gas possessing very large velocities increases the root mean square velocity without affecting the most probable velocity.
Assertion: Two different gases having same temperature always have molecules with same RMS
speed.
Reason: The average translational kinetic energy per mole for each gas is (where, Boltzmann constant, temperature in Kelvin).
Assertion: The pressure of a gas filled in a cylinder fitted with an immovable piston is increased by raising its temperature.
Reason: On raising the temperature, greater momentum is transferred to the wall of the container per second.
Assertion: It is possible for both the pressure and volume of a monoatomic ideal gas of a given amount to change simultaneously without causing the internal energy of the gas to change.
Reason: The internal energy of an ideal gas of a given amount remains constant if temperature does not change. It is possible to have a process in which pressure and volume are changed such that temperature remains constant.
Assertion: Equal moles of helium and oxygen gases are given equal quantities of heat at constant volume. There will be a greater rise in the temperature of helium as compared to that of oxygen.
Reason: The molecular weight of oxygen is more than the molecular weight of helium.
