Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
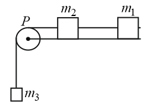
A system consists of three masses and connected by a string passing over a pulley . The mass hangs freely and and are on a rough horizontal table (the coefficient of friction). The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The downward acceleration of mass is (assume, ),
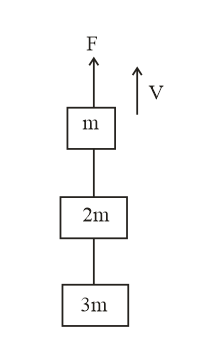
Three blocks with masses and are connected by strings as shown in the figure. After an upward force is applied on block , the masses move upward with constant speed . What is the net force on the block of mass ? is the acceleration due to gravity)
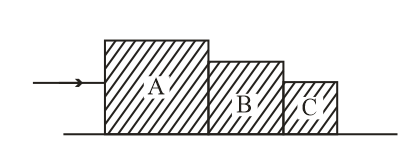
Three blocks and of masses and , respectively, are in contact on a frictionless surface as shown. If a force of is applied on the block, then the contact force between and is,
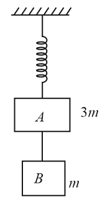
Two blocks and of masses and , respectively, are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a massless spring as shown in figure. The magnitudes of acceleration of and immediately after the string is cut are, respectively,
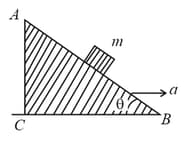
A block of mass is placed on a smooth inclined wedge of inclination as shown in the figure. The wedge is given an acceleration towards the right. The relation between and for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is,
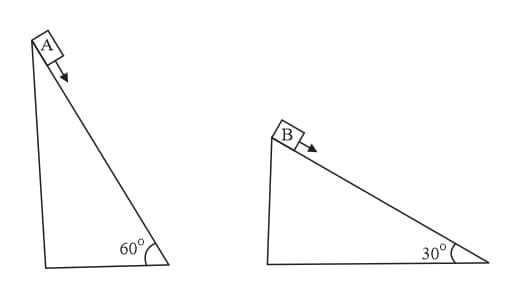
Two fixed frictionless inclined planes making an angle and with the vertical are shown in the figure. Two blocks and are placed on the two planes. What is the relative vertical acceleration of with respect to ?
A mass of is suspended vertically by a rope from the roof. When a horizontal force is applied on the mass, the rope deviated at an angle of at the roof point. If the suspended mass is at equilibrium, the magnitude of the force applied is (Take, )
Two forces and of magnitude and , respectively, are at an angle with each other. If the force is doubled, then their resultant also gets doubled. Then, the angle is
