Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 10: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Rotational Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with Hints & Solutions
A particle of mass is moving horizontally at speed perpendicular to a uniform rod of length and mass, . The rod is hinged at centre and can freely rotate in horizontal plane about a fixed vertical axis passing through its centre . The hinge is frictionless. The particle strikes and sticks to the end of the rod. The angular speed of the system just after the collision is,
If is the radius vector and is momentum, the angular momentum is given by, . Which of the graphs show correctly the variation of with ?
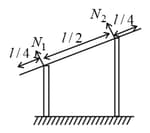
A uniform rod of length is placed symmetrically on two walls as shown in figure. The rod is in equilibrium. If and are the normal forces exerted by the walls on the rod, then,
Assertion: If two different axes are at same distance from centre of mass of a rigid body, then moment of inertia of the given rigid body about both axes will always be same.
Reason: A thin uniform rod is undergoing fixed axis rotation about one of its ends with variable angular acceleration. Then, the acceleration vector of any two moving points on the rod cannot be parallel at an instant of time.
Assertion: A rigid disc rolls without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface with uniform angular velocity. Then, the acceleration of lowest point on the disc is zero.
Reason: For a rigid disc rolling without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface, the velocity of the lowest point on the disc may be non-zero.
Assertion: A thin uniform rod is undergoing fixed axis rotation about one of its ends with variable angular acceleration. The acceleration vector of any two moving points on the rod can not be parallel at any instant of time.
Reason: For a rod undergoing fixed axis rotation, the velocity of any two moving points on the rod at different distances from the centre of rotation is different.
Assertion: A rigid disc rolls without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface with uniform angular velocity. Then the acceleration of the lowest point on the disc is zero.
Reason: For a rigid disc rolling without slipping on a fixed rough horizontal surface, the velocity of the lowest point on the disc is always zero.
Assertion: A uniform cubical block (of side ) undergoes translational motion on a smooth horizontal surface under action of horizontal force as shown. Under the given condition, the horizontal surface exerts normal reaction non-uniformly on lower surface of the block.
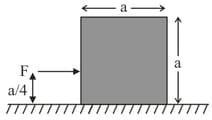
Reason: For the cubical block given in statement , the horizontal force has tendency to rotate the cube about its centre in clockwise sense. Hence, the lower right edge of cube presses the horizontal surface harder in comparison to the force exerted by lower left edge of cube on horizontal surface.
