Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 14: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with Hints & Solutions
A ball of mass and radius is released in a viscous liquid. The value of its terminal velocity is proportional to :
In Poiseuilli's method of determination of coefficient of viscosity, the physical quantity that requires greater accuracy in measurement is
What is the velocity of a metallic ball of radius falling in a tank of liquid at the instant when its acceleration is one-half that of a freely falling body ? (The densities of metal and of liquid are and respectively, and the viscosity of the liquid is ).
According to Newton, viscous force is given by
where coefficient of viscosity, so dimensions of will be :
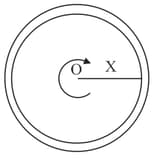
The diagram shows a cup of tea seen from above. The tea has been stirred and is now rotating without turbulence. A graph showing the speed with which the liquid is crossing points at a distance from along a radius would look like
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of .
If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is
In a vessel equal masses of alcohol (sp. gravity ) and water are mixed together. A capillary tube of radius is dipped vertically in it. If the mixture rises to a height in the capillary tube, the surface tension of the mixture is
A spherical soap bubble of radius is formed inside another of radius . If a single soap bubble is formed which maintains the same pressure difference as inside the smaller and outside the larger bubble, the radius of this bubble is
