Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 4: EXERCISE-4
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 4: EXERCISE-4
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 10: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 4: EXERCISE-4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 4: EXERCISE-4 with Hints & Solutions
For the two parallel reactions and , show that the activation energy ' for the disappearance of is given in terms of activation energies and for the two paths by
For the mechanism
Derive the rate law using the steady-state approximation to eliminate the concentration of .
Assuming that , express the pre-exponential factor and for the apparent second-order rate constant in terms of and and and for the three steps.
The decomposition of a compound , at temperature according to the equation
is the first order reaction. After minutes from the start of decomposition in a closed vessel, the total pressure developed is found to be and after a long period of time the total pressure observed to be . Calculate the total pressure of the vessel after minute, if volume of liquid is supposed to be negligible. Also calculate the time fraction
Given : Vapour pressure of at temperature .
A certain reactant is getting converted to in solution. The rate constant of this reaction is measured by titrating a volume of the solution with a reducing reagent which only reacts with and . In this process, it converts to and to . At , the volume of the reagent consumed is and at , the volume used up is . Calculate the rate constant of the conversion of to assuming it to be a first order reaction.
The reaction (aq) is monitored by measuring optical rotation of reaction mixture at different time interval. The species $A, B$ and $C$ are optically active with specific rotations and Respectively. Starting with pure A if the value of optical rotations was found to be after Minutes and optical rotations was After infinite time. Find the rate constant for order conversion of A into B and C.
The reaction A proceeds in parallel channels  Suppose the half life values for the two branches are minutes and minutes, what is the overall half-life value?
Suppose the half life values for the two branches are minutes and minutes, what is the overall half-life value?
The catalytic decomposition of formic acid may take place in two ways :
(a)
(b)
The rate constant and activation energy for reaction (a) are at and kcal . respectively and for reaction (b) are at and respectively. Find the temperature which will give a product made up of equimolar quantities of water vapour, carbon monoxide, hydrogen and carbon dioxide.
For the following first order gaseous reaction
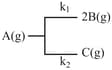
The initial pressure in a container of capacity litres is . Pressure at time is and after infinite time it becomes atmosphere. Find the rate constant and for the appropriate reactions.
