Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 32: Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with Hints & Solutions
Two particles have identical charges. If they are accelerated through identical potential differences, then the ratio of their deBroglie wavelength would be
The wavelength of de-Broglie waves associated with neutrons at room temperature is
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is . Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero?
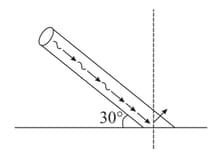
The number of photons that strike per second on a totally reflecting screen (as shown in figure), so that a force of is exerted on the screen, is approximately.
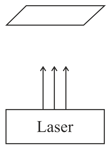
An impulse laser may be treated as a source of photons that are emitted during the time interval of the pulse which is followed by a time interval when no photons are produced. Pulses are periodically repeated. A laser beam of diameter microns is directed upward and is perpendicular to the thin foil surface which has an index of reflection (see the sketch of the experiment). The index of reflection of the surface is the ratio of the reflected energy to the impact energy. A pulse with duration of has a total energy of . What is the mass of the piece of foil that can be supported in the air solely by the light pressure of the laser beam?
Which of the following are not electromagnetic wave?
Arrange the following electromagnetic radiations per quantum in the order of increasing energy
Blue light
Yellow light
-ray
Radiowave
Microwave oven acts on the principle of transferring electrons from lower to
