Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 27: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with Hints & Solutions
Match the following:
| (i) | magnetic flux | (a) | tesla |
| (ii) | magnetic flux density | (b) | weber |
| (iii) | relative permeability | (c) | no unit |
| (iv) | magnetic field intensity | (d) | amper/meter |
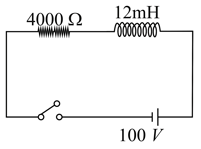
When current changes from to in , an e.m.f. of is induced in a coil. The coefficient of self-induction of the coil is
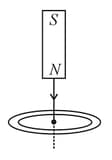
Consider a metal ring kept on a horizontal plane. A bar magnet is held above the ring with its length along the axis of the ring. If the magnet is dropped freely the acceleration of the falling magnet is ( is acceleration due to gravity)
In the inductive circuit given in fig. the current rises after the switch is closed. At instant, when the current is . Then potential difference across the inductor is :-
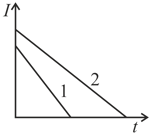
Two identical inductance carry currents that vary with time according to linear laws (as shown in figure). In which of two inductance is the self induction emf greater?
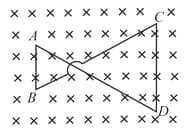
A conducting wire frame is placed in a magnetic field which is directed into the paper. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate. The directions of induced current in wires and are :-
In circuit when ammeter is connected it reads current if a student uses ammeter the reading in the ammeter will be
In an circuit, the capacitor has maximum charge . The value of is