Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 13: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4 with Hints & Solutions
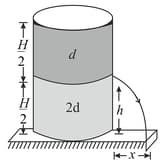
A container of large uniform cross-sectional area resting on a horizontal surface, holds two immiscible, non-viscous and incompressible liquids of densities and each of height as shown in figure. The lower density liquid is open to the atmosphere having, pressure
(i) A homogeneous solid cylinder of length crosssectional area is immersed such that if floats with its axis vertical at the liquid-liquid interface with length in the denser liquid. Determine:
(a) the density of the solid,
(b) the total pressure at the bottom of the container.
(ii) The cylinder is removed and the original arrangement is restored. A tiny hole of area s is, punched on the vertical side of the container at a height Determine:
(a) the initial speed of efflux of the liquid at the hole
(b) the horizontal distance travelled by the liquid initially, and
(c) the height at which the hole should be punched so that the liquid travels the maximum distance) initially. Also calculate (Neglect the air resistance in these calculations)
An open rectangular tank of dimension containing water upto a height of is accelerated horizontally along the longer side.
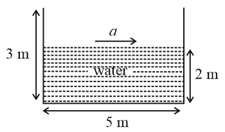
(i) Determine the maximum acceleration that can be given without spilling the water.
(ii) Calculate the percentage of water split over, if this acceleration is increased by
(iii) If initially, the tank is closed at the top and is accelerated horizontally by find the gauge pressure at the bottom of the front and rear walls of the tank.
A ship sailing from sea into a river sinks and on discharging the cargo rises On proceeding again into sea the ship rises the Find the specific gravity of sea-water assuming the faces of ship are vertically along the line of sea-water.
A conical vessel without a bottom stands on a table. A liquid is poured with the vessel & as the level reaches , the pressure of the liquid raises the vessel. The radius of the base of the vessel is and half angle of the cone is and the weight of the vessel is What is the density of the liquid?
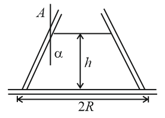
A cylindrical rod of length and density floats vertically in a liquid of density as shown in figure.
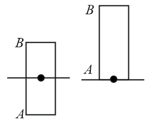
(i) Show that it performs SHM when pulled slightly up and released and find its time period. Neglect change in liquid level.
(ii) Find the time taken by the rod to completely immerse when released from position shown in second figure. Assume that it remains vertical throughout its motion. (take )
On the opposite sides of a wide vertical vessel filled with water two identical holes are opened, each having the cross-sectional area The height difference between them is equal to Find the resultant force of reaction of the water flowing out of the vessel.
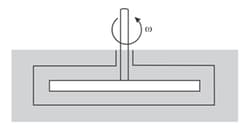
A thin horizontal disc of radius is located with in a cylindrical cavity filled with oil whose viscosity (figure). The distance between the disc and the horizontal planes of the cavity is equal to Find the power developed by the viscous forces acting on the disc when it rotates with the angular velocity The end effects are to be neglected.
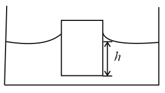
9A cube with a mass completely wettable by water floats on the surface of water. Each side of the cube is What is the distance h between the lower face of cube and the surface of the water if surface tension is Take density of water as Take angle of contact is zero.