Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 18: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with Hints & Solutions
If the intermolecular forces vanish away, the volume occupied by the molecules contained in . water at standard temperature and pressure will be given by:
In a process the density of a gas remains constant. If the temperature is doubled, then the change in the pressure will be:
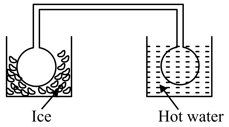
Two identical glass bulbs are interconnected by a thin glass tube at . A gas is filled at N.T.P. in these bulb is placed in ice and another bulb is placed in hot bath, then the pressure of the gas becomes times. The temperature of hot bath will be:
As shown, a piston chamber of cross-section area is filled with an ideal gas. A sealed piston of mass is right at the middle height of the cylinder at equilibrium. The friction force between the chamber wall and the piston can be ignored. The mass of the rest of the chamber is . The atmosphere pressure is . Now slowly pull the piston upwards, find the maximum value of such that the chamber can be lifted off the ground. The temperature remains unchanged.

A gas has volume and pressure . The total translational kinetic energy of all the molecules of the gas is
molecules of a gas strike a target of area at angle to normal and rebound elastically with speed . The impulse normal to wall per molecule is: [Given: mass of molecule ]
The density in grams per litre of ethylene at STP is
, and moles of monatomic, diatomic and non-linear polyatomic gases (which do not react chemically with each other), respectively, are mixed at room temperature. The equivalent degree of freedom of the mixture is
