Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Laws of Motion, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
A solid sphere of mass is resting inside a cube as shown in figure. The cube is moving with a velocity . Here is the time in second. All surface are smooth. The sphere is at rest with respect to the cube. The total force exerted by sphere on the cube is Nuwton. Value of is
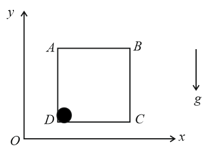
If contact force between and is and between and is . Find out .
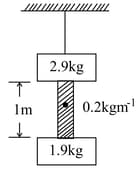
Two blocks of mass and are suspended from a rigid support by two inextensible wires each of length (see figure). The upper wire has negligible mass and the lower wire has a uniform mass of . The whole system of blocks, wires and support have an upward acceleration of . The acceleration due to gravity is . IF the tension at the midpoint of the lower and upper wires are and respectively. Find value of
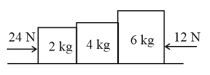
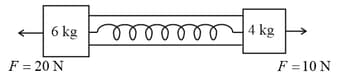
A dynamometer is attached to two blocks of masses and . Forces of and are applied on the blocks as shown in figure. The dynamometer reading is given as . Find the value of .
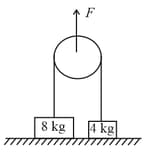
Two block of mass and are connected by a string as shown. They are initially at rest on the floor, when a force of is applied on the pulley in upward direction. If acceleration of the blocks are and , find value of
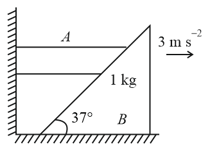
Find force in newton which mass exerts on mass if is moving towards right with . All surfaces are smooth and
A thin rod of length is fixed in a vertical position inside a train, which is moving horizontally with constant acceleration . A bead can slide on the rod, and friction coefficient between them is . If the bead is released from rest at the top of the rod, find the time in second when it will reach at the bottom.
A light rod of length is suspended from the ceiling horizontally by means of two vertical wires of equal length tied to its ends. One of the wires is made of steel and is of cross-sectional area and the other is of brass of cross-sectional area Find out the distance from steel wire (in metre) of position along the rod at which a weight may be hung to produce equal stresses in both wires. : for steel and for brass
