Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 30: Ray Optics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 4: Exercise-4 with Hints & Solutions
One side of radius of curvature of a convex lens of refractive index and focal length is silvered. It placed on a horizontal surface with silvered surface is contact with it. Another convex lens of focal length is fixed coaxially above. A luminous point object on the axis gives rise to an image coincident on it . Find its height above the upper lens.
A right angle prism of refractive index has a plane of refractive index cemented to its diagonal face. The assembly is in air. The ray is incident on .
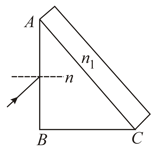
(i) Calculate the angle of incidence at for which the ray strikes the diagonal face at the critical angle.
(ii) Assuming , calculate the angle of incidence at for which the refracted ray passes through the diagonal face undeviated. ()
A glass wedge with a small angle of refraction is placed at a certain distance from a converging lens with a focal length , one surface of the wedge being perpendicular to the optical axis of the lens. A point sources of light is one the other side of the lens at its focus. The rays reflected from the wedge (not from base) produce, after refraction in the lens, two images of the source displaced with respect to each other by . Find the refractive index of the wedge glass. [Consider only paraxial rays].
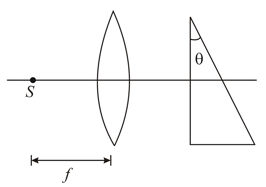
A log solid cylindrical glass rod of refractive index is immersed in a liquid of refractive index . The ends of the rod are perpendicular to the central axis of the rod. A light enters one end of the rod at the central axis as shown in the figure. A light enters one end of the rod at the central axis as shown in the figure. Find the maximum value of angle for which total internal reflection occurs inside the rod?
In the figure shown is converging lens of focal length and is a concave mirror of radius of curvature . A point object is placed in front of the lens at a distance . and are optical axes of the lens and mirror respectively. Find the coordinates of the final image formed by this system taking as origin. The distance between & is .
An equilateral prism deviates ray through for two angles of incidence differing by . Find of the prism.
The figure shows the path of a ray passing through an equiangular prism . It is incident on face at an angle slightly greater than the critical angle for total internal reflection. If the angle shown in the figure is . Calculate the Refractive index of the material of the prism.
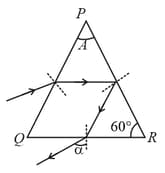
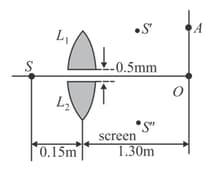
In the figure shown is a monochromatic point source emitting light of wavelength . A thin lens of circular shape and focal length is cut into two identical halves and by a plane passing through a diameter. The two halves are placed symmetrically about the central axis SO with a gap of . The distance along the axis from to and is , while that from and to is .
The screen at is normal to SO. (i) If the third intensity maximum occurs at the point on the screen, find the distance OA. (ii) If the gap between and is reduced from its original value of , will the distance OA increase decrease or remain the same?