Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Properties of Matter, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Properties of Matter, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 15: Thermal Properties of Matter, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Properties of Matter, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with Hints & Solutions
The temperature of an isotropic cubical solid of length , density and coefficient of linear expansion is increased by . Then at higher temperature, to a good approximation:-
A glass rod when measured with a zinc scale, both being at , appears to be of length . If the scale shows correct reading at , then the true length of glass rod at and are:-
Two fine steel wires, fastened between the projections of a heavy brass bar, are just taut when the whole system is at . What is the tensile stress in the steel wires when the temperature of the system is raised by ?
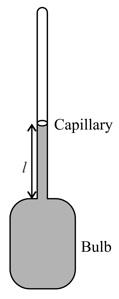
In a mercury-glass thermometer the cross-section of the capillary portion is and the volume of the bulb is at . If and are the coefficients of linear and cubical expansion coefficients of glass and mercury respectively then length of mercury in the capillary at temperature is (Ignore the increase in cross-sectional area of capillary)
of steam at is mixed with of ice at . Choose correct alternative/s):-(Given , ).
moles of an ideal triatomic linear gas undergoes a process in which the temperature changes with volume as where is a constant. Choose incorrect alternative:-
Four moles of hydrogen, two moles of helium and one mole of water vapour form an ideal gas mixture. What is. the molar specific heat at constant pressure of mixture ?
A inert gas obeys the law constant. For what value of , it has negative molar specific heat-
