Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 17: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
In the given figure an ideal gas changes its state from to state by two paths and .
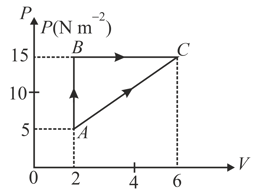
(i) The internal energy of gas at is and amount of heat supplied to change its state to through the path is . Calculate the internal energy at .
(ii) The internal energy of gas at is . Find the amount of heat supplied to the gas from to .
The pressure in monoatomic gas increases linearly from to when its volume increases from to .
(i) If work done by the gas is then find the value of .
(ii) If increase in internal energy is then find the value of .
(iii) If amount of heat supplied is then find the value of .
(iv) If molar specific heat of the gas is then find the value of .
On mole of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in figure.
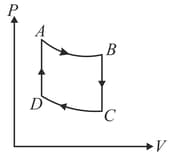
: Adiabatic expansion : Cooling at constant volume
: Adiabatic compression
: Heating at constant volume
The pressure and temperature at , etc., are denoted by etc., respectively. Given that , and .
Calculate the following quantities : (i) The work done by the gas in the process
(ii) The heat lost by the gas in the process
(iii) The temperature . (Given : )
Three moles of an ideal gas at pressure, and temperature is isothermally expanded to twice its initial volume. It is then compressed at constant pressure to its original volume. Finally gas is compressed at constant volume to its original pressure . If the net work done by the gas, and net heat support to the gas during the complete process is and respectively then fine .
Two moles of helium gas are initially at temperature and occupy a volume of . The gas is first expanded at constant pressure until the volume is doubled. Then it undergoes an adiabatic change until the temperature returns to its initial value. (i) If the final volume and pressure of the gas are and then the find . (ii) What is the work done by the gas?
A gaseous mixture enclosed in a vessel of volume consists of one gram mole of gas. with an another gas with at a certain temperature . The gram molecular weight of the gases and are and respectively. The gases and do not react with each other and are assumed to be ideal. The gaseous mixture follows the equation constant, in adiabatic process. Find the number of gram moles of the gas in the gaseous mixture.
One mole of an ideal gas is heated isobarically from the freezing point to the boiling point of water each under normal pressure. Find out the work done by the gas the change in its internal energy. The amount of heat involved is .
An ideal gas at is enclosed in a adiabatic vertical cylinder having are of cross section , between two light movable pistons as shown in the figure. Spring with force constant is in a relaxed state initially. Now the lower piston is moved upwards a height , being the initial length of gas column. It is observed that the upper piston moves up by a distance . Find taking for the gas to be Also find the final temperature of the gas.